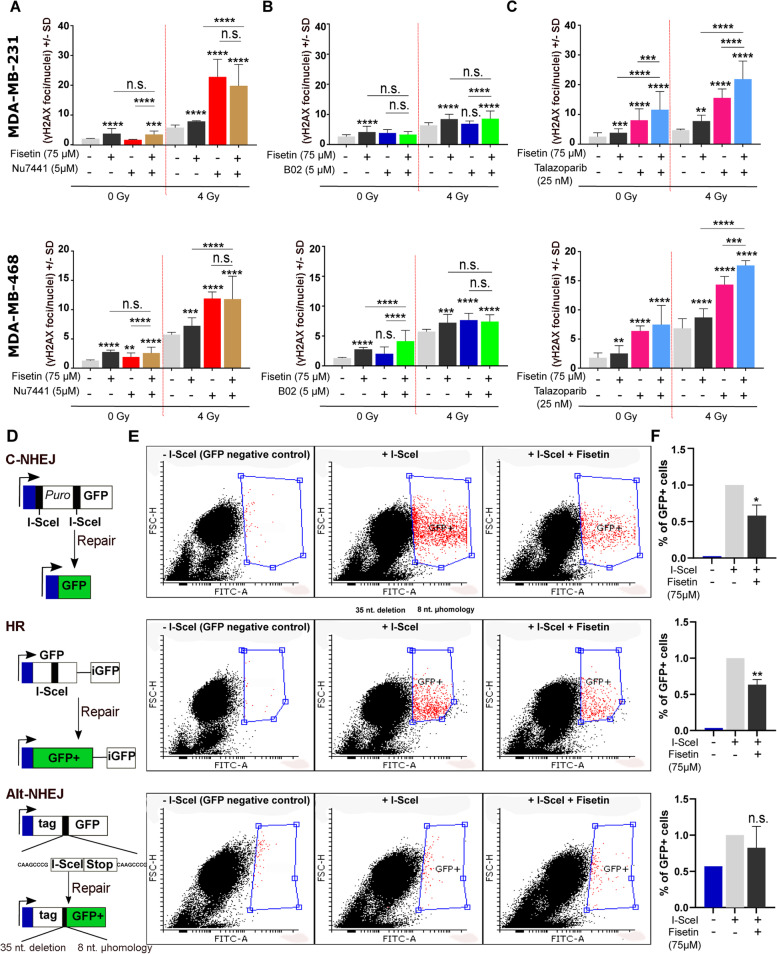
Fig. 5.
Fisetin inhibits DSB through the HR and C-NHEJ repair pathways. A-C MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with or without fisetin (75 µM) for 22 h and followed by treatment with or without DNA-PKcs inhibitor (NU7441, 5 µM), Rad51 inhibitor (B02, 5 µM) or PARP inhibitor (Talazoparib, 25 nM) for 2 h. The DMSO concentration in cells treated with different inhibitors was kept similar. Thereafter, cells were mock irradiated or irradiated 4 Gy and γH2AX was performed 24 h after IR. γH2AX foci per nuclei were counted using FoCo software. The data are presented as the mean number of foci per nuclei ± S.D. The asterisks indicate significant inhibition of DSB repair shown by increased mean residual γH2AX ± SD after treatment with indicated inhibitors compared to DMSO treated/ 4 Gy irradiated control condition or compared between indicated groups from at least 300 nuclei in MDA-MB-231 cells and MDA-MB-468 cells from at least 3 independent experiments (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001), ****p < 0.0001; students t-test). D U2OS cells harboring different DNA repair constructs including HR, C-NHEJ and Alt-NHEJ were used. E The cells were either transiently transfected with an inducible endonuclease I-SceI plasmid (800 ng/ml) or not transfected as a negative control. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated with or without fisetin (75 µM, 24 h). Nuclear translocation of I-SceI was induced by 100 ng/ml triamzinolonacetonid and twenty-four hours later the percentage of GFP positive cells were determined using FACS. F The bar graphs show the mean percentage of GFP positive cells ± SD from 4 independent experiments normalized to DMSO treated control condition. Asterisks indicate inhibition of the indicated repair pathway by fisetin treatment (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; students t-test). The data shown for GFP-negative control cells is the mean from 2 independent experiments