Figure 5.
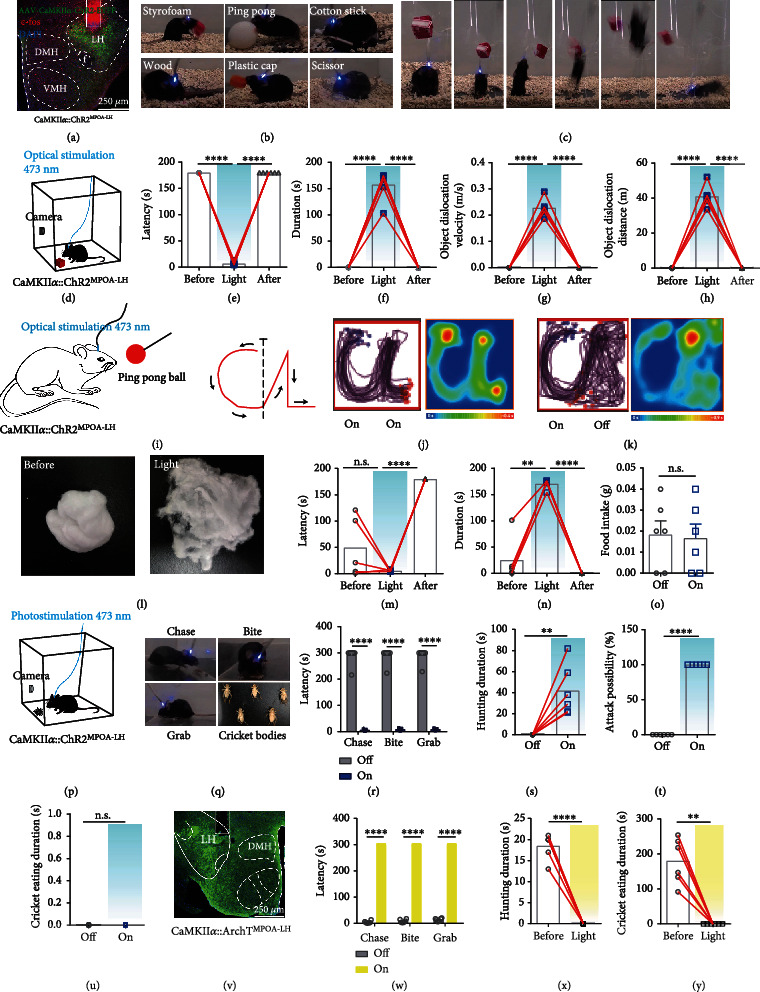
CaMKIIαMPOA-LH projection induces object exploration and hunting but not feeding behavior. (a) Representative image of MPOA-LH axons (green) and immunolabeled Fos protein (red), scale bar, 250 μm. (b) CaMKIIα::ChR2MPOA–LH mice showed active interaction with different objects. (c) Mice showed a sequential posture of leaping and jumping up to reach an impending object. (d) Schematic of object dislocation behavior. (e–h) Effects of CaMKIIα::ChR2MPOA-LH activation on object exploration behavior: latency (e), duration (f), average object dislocation velocity (g), and object dislocation distance (h) (n = 6, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001). (i–k) Effect of optical stimulation of MPOA-LH axon terminal upon chasing. Mice follow the moving ball along designed route (i); cumulative traces of the mouse trace and average heat map, the light was delivered constantly (j); cumulative traces of navigation pathways and mean heat map, the light was withdrawn immediately when finished “C” (k). (l–n) Effect of MPOA-LH projection activation on biting: representative image of cotton balls (l), latency (m), and duration of biting cotton (n) (n = 6, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001). (o) Food intake in three min (paired t-test, P = 0.7926). (p) The experimental arena for hunting. (q–u) Effects of optical stimulation CaMKIIαMPOA-LH axon terminals on hunting behavior of well-fed mice: representative video snapshots of mice showed a sequential posture of hunting a cricket and the dead bodies (q), latency of each procedure when hunting (r), duration of hunting(s), attack possibility of 5 crickets (t), and cricket eating duration (u) (n = 6, paired t-test, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗P < 0.01). (v) Representative image of CaMKIIα::ArchTMPOA-LH axon terminals and optical fiber cannula position, scale bar, 200 μm. (w and x) Effects of optical inhibition of the CaMKIIα::ArchTMPOA-LH axon terminal on hunting behavior of food-restricted mice: latency of each process (w) and duration of hunting a cricket (x) and cricket eating duration (y) (n = 6, paired t-test, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗P < 0.01).
