Figure 4.
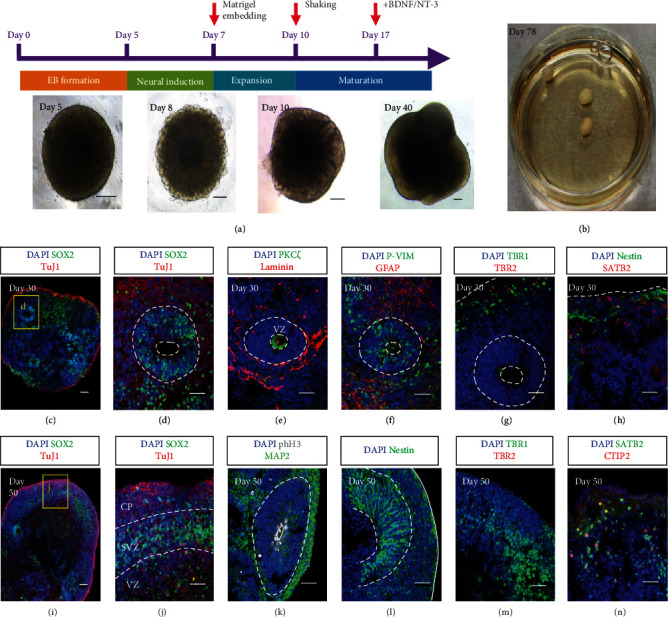
Generation of cerebral organoids. (a) Schematic diagrams illustrating the protocol to generate cerebral organoids. Differential interface contrast (DIC) images in the lower panel show the morphology of the organoid changes on day 5, day 8, day 10, and day 40. (b) The photo displays three cerebral organoids at day 78 in a 3 cm dish. (c–h) Confocal images of the cryosections of cerebral organoids at day 30. The organoids express the neural stem cell marker SOX2 in a rosette structure and pan neural marker TuJ1 in the region beyond the rosette (c, d; (d) is the magnified image of the boxed area in (c)). The apical- (PKCξ) basal (Laminin) structure indicates polarized cortical neuroepithelia (e). Radial glial cells expressing the combination of P-Vimentin (P-VIM) and GFAP distribute both in and out of the proliferative zone (f). Deep-layer neuron marker TBR1 and intermediate progenitor cell marker TBR2 are found at the edge of the organoids (g). Late-born neurons are marked by SATB2, while neural stem cells are revealed by Nestin within the same region (h). (i–n) Confocal images of the cryosections of cerebral organoids at day 50. A lobe structure with an identified SOX2-expressing layer is characterized by the cortical plate (CP), subventricular zone (SVZ), and ventricular zone (VZ) (i–j). Apical mitoses are revealed by phospho-histone H3 in a polarized rosette surrounded by MAP2+ cells (k). The Nestin+ cells are abundant both in the rosette and along the lobe periphery (l). Neurons are expressing TBR1, but TBR2 is found to be scarce (m). The signals of the surface cortical neuron marker SATB2 and deep-layer cortical neuron marker CTIP2 are shown (n). Scale bars, 50 μm (c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n) and 200 μm (a).
