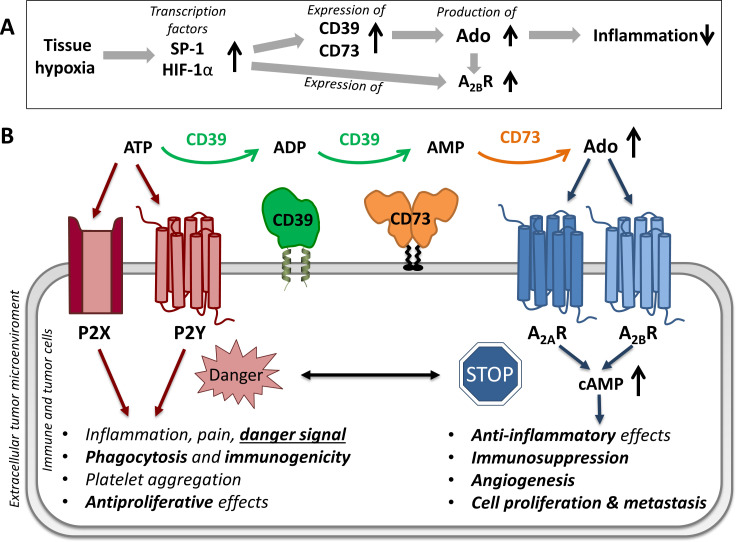
Figure 1.
Hypoxia-induced purinergic signaling. (A) Tissue hypoxia increases the release of transcription factor SP-1 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), which leads to an increase in the expression and enzymatic capacity of adenosine-producing ectonucleotidases and to an increased expression of adenosine A2B receptors (A2BR), resulting in reduced inflammation.2 (B) Effects of extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP, danger-associated molecular pattern molecule) and adenosine via purinergic P2 and adenosine A2A and A2B receptors. ATP is dephosphorylated by a concerted action of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 (NTPDase1, CD39) and ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73) to adenosine. SP-1, specific protein 1; CD, cluster of differentiation.