|
-
✓
Negatively regulates IL-2 and IFNγ by lymphocytes and TNF-α and IL-12 by macrophages
-
✓
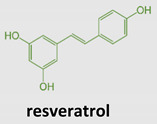
Reduced immune-inflammatory responses
-
✓
Activates Sirt1 which negatively interferes with the TLR4/NF-κB/STAT signal, with reduced cytokines secretion from inactivated immune cells and macrophage/mast cell-derived pro-inflammatory factors.
-
✓
Activates macrophages, T cells, and NK cells
-
✓
Regulates CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell suppressive functions
-
✓
Activates Sirt1 which deacetylates STAT3 interfering with th17 lymphocyte differentiation
-
✓
Restores T-cell function targeting the immune-checkpoint signaling PD-1/PD-L1
-
✓
Activates NK cells through AKT- and mTORC2-mediated c-Myb upregulation
-
✓
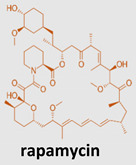
Provides general inhibitory effects on the immune system
-
✓
Ameliorates some immune functions in the elderly, response to vaccination and improved outcomes from infections
-
✓
Inactivates T and B lymphocytes
-
✓
Impairs lipid to glucose metabolism and immune suppression in long-term use
-
✓
Extends lifespan and delay aging in model organisms
-
✓
Reduces p16INK4A protein expression and increases collagen VII protein levels in the skin
-
✓
Reduces the negative effects on the immune system in COVID-19 patients
-
✓
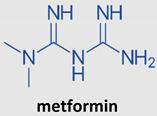
Exerts direct immunomodulatory effect on immune cells by AMPK induction and mTORC1 inhibition
-
✓
Promotes health immunity via an H3K4 methyltransferase/demethylase complex, downregulating some targets, including mTOR and S6 kinase
-
✓
Increases the differentiation of naïve T cells into both regulatory and memory T cells, while decreasing the ability of neutrophils to initiate in NETosis.
-
✓
Exerts immunomodulatory effects and contributes to the reduction of lung metastases of melanoma cell
-
✓
Increases the number and function of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and inhibits oxidative phosphorylation in B cells
-
✓
Reduces the stability and localization of PD-L1
-
✓
Contributes to the improvement of CTLs against cancer cells
-
✓
Reduces the burden of autoimmune diseases in several animal models and some human studies
|



