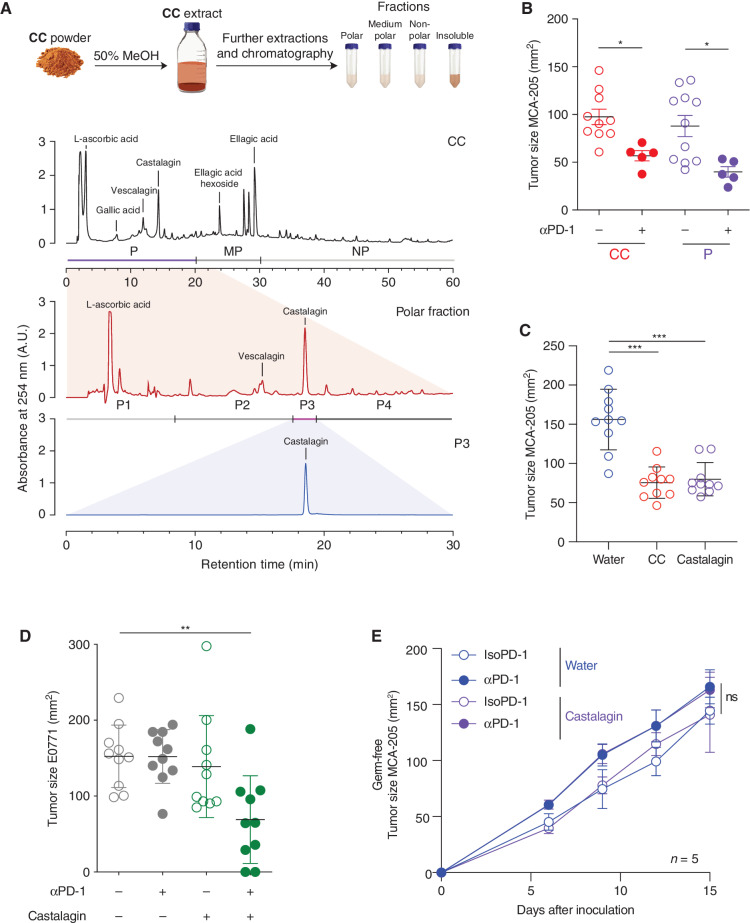
Figure 3.
Identification of castalagin as the bioactive compound of CC with similar antitumor activity. A, Schematic of the CC fractionation procedure and summary of chromatograms (λ = 254 nm) showing the isolation of bioactive fractions from CC: CC extract (top chromatogram) containing fractions polar (P), medium polar (MP), and nonpolar (NP). Representation of the polar fraction (middle chromatogram) containing subfractions P1–4 and polar subfraction 3 (P3; bottom chromatogram). B, Tumor size at sacrifice of mice bearing MCA-205 treated with daily oral gavage with CC or P fraction (n = 10 mice/group). C, Tumor size at sacrifice in the MCA-205 model after daily oral supplementation with CC, castalagin at the standard concentration (0.85 mg/kg per mouse), or water (n = 10 mice/group). D, Tumor size at sacrifice of E0771-bearing SPF mice after sequential injections of αPD-1 or IsoPD-1 and a daily oral gavage with water or castalagin at the standard concentration (0.85 mg/kg per mouse; n = 10 mice/group). E, MCA-205 tumor kinetics in mice reared under GF conditions treated with sequential injections of αPD-1 or IsoPD-1 and a daily oral gavage with water or castalagin (n = 5 mice/group). Means ± SEM are represented in B–E. ns, nonsignificant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.