Figure 5.
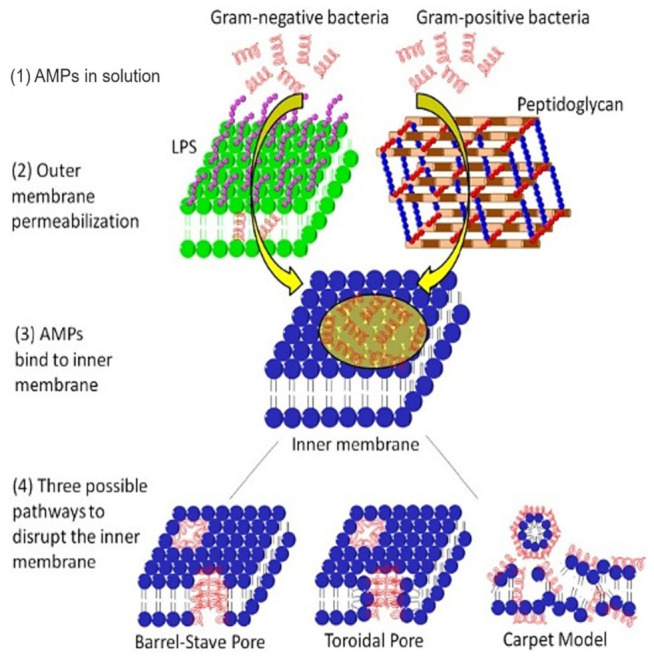
Mechanism of action of AMPs on the membrane system of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. In Gram-negative bacteria, the AMP outreach the cytoplasmic membrane via permeabilizing the outer membrane, while in Gram-positive bacteria, the AMP directly disperses through nano ranged pores of the peptidoglycan layer. After binding to the inner membrane, APMs can create three types of pores (barrel-stave pore, toroidal pore, or carpet model). Adapted from Jianguo et al. 2017, [131].
