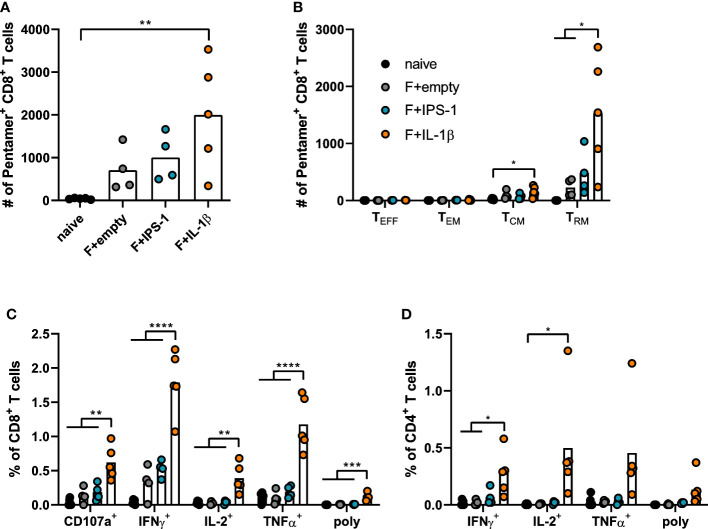
Figure 2.
Vaccine-induced T cell responses in the lung. BALB/cJRj mice were immunized as described above and lung lymphocytes were analyzed 49 days later. Counts of F85-93 pentamer+ CD8+ T cells per lung (A) and counts of specific memory T cell subsets (B) are shown; effector T cells, TEFF, KLRG1+CD127-; effector memory T cells, TEM: KLRG1+CD127+; central memory T cells, TCM: KLRG1-CD69-CD103-CD127+; TRM: KLRG1-CD127+/-CD69+CD103+; gating scheme in Supplementary Figure 2 . (C, D) Lung lymphocytes were restimulated with MHC-class I and class II peptides derived from the F protein and the functionality of CD8+ T cells (C) and CD4+ T cells (D) was detected via extracellular staining for CD107a and intracellular cytokine staining (poly; for CD8+: CD107a+IFNγ+IL-2+TNFα+; for CD4+: IFNγ+IL-2+TNFα+; gating strategy in Supplementary Figure 3 ). Bars represent group means overlaid with individual data points. n=4-5. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey´s post Test. *p<0.05, ** p<0.005, *** p<0.0005, **** p<0.0001.