FIGURE 2.
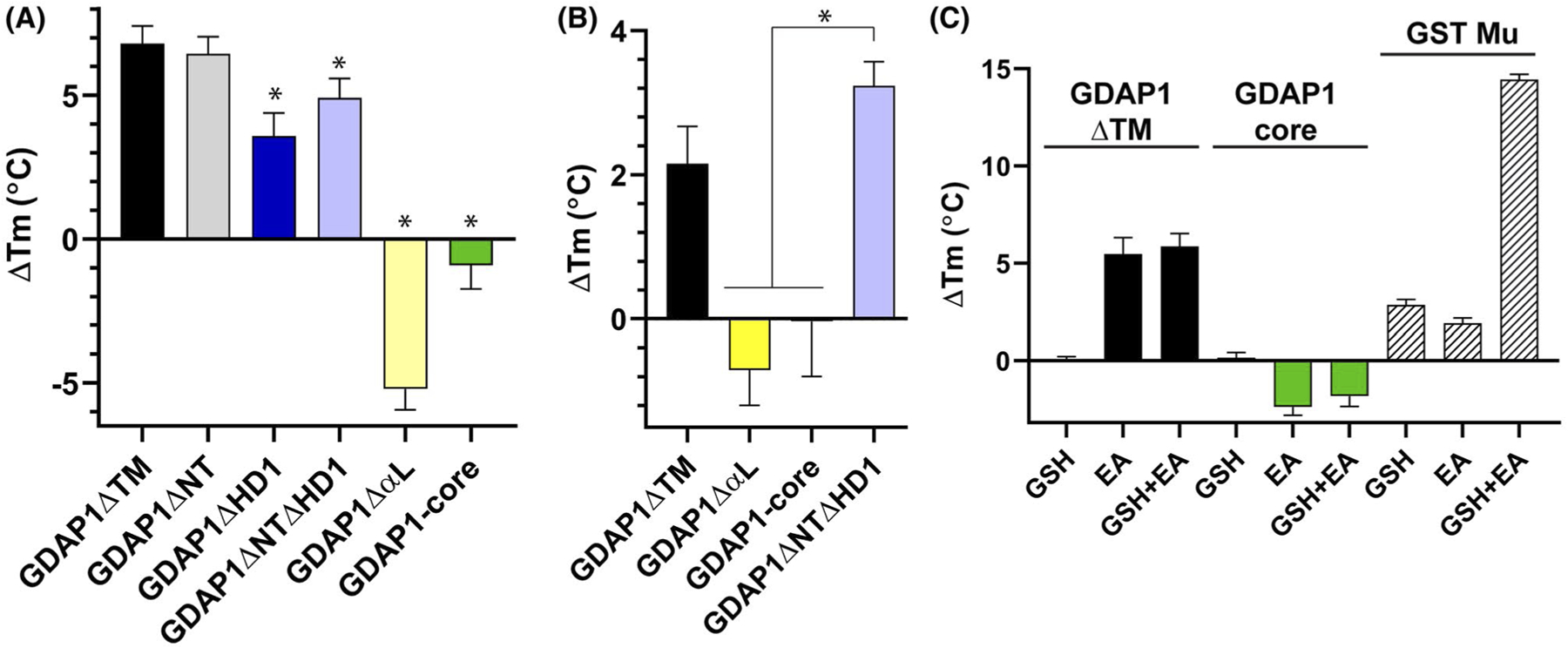
The α-Loop and HD1 are involved in substrate binding in vitro. A, Differential scanning fluorimetry of GDAP1 constructs comparing their melting temperatures with and without the addition of 2 mM Ethacrynic Acid, as described in Materials and Methods. Data are the average of 4 independent experiments with error bars representing standard deviation. Statistically significant (*) indicate a P < .01 using a two-way ANOVA. B, Differential scanning fluorimetry with 0.5 mM ethacrynic acid indicates that the presence of the α-loop plays an important role in substrate binding even at lower substrate concentrations. C, Differential scanning fluorimetry looking at the melting temperature shifts of GDAP1 constructs upon the addition of 1 mM GSH, 1 mM ethacrynic acid, or both 1 mM GSH and 1 mM Ethacrynic Acid. Data are representing four independent experiments with error bars showing standard deviation
