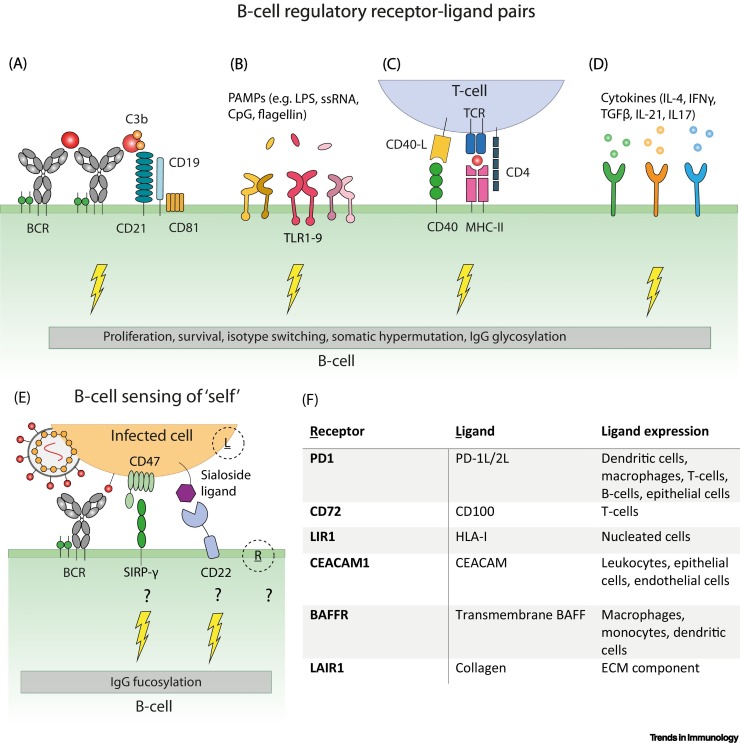
Figure I.
Immunoregulatory receptor–ligand pairs involved in fine-tuning the B cell response in humans.
(A–D) Recognition of antigen by B cell receptors (BCRs) results in BCR clustering and crosslinking with the CD19–CD21 coreceptor complex thereby increasing BCR mediated signaling [4,95]. In addition, signaling via Toll-like receptors (TLRs), CD40–CD40L, and cytokine receptors is important for B cell differentiation, isotype switching, and IgG glycosylation [4]. (E) A similar signaling axis might be involved in regulating IgG fucosylation through sensing of ‘self’ (e.g., CD47 or sialoside ligands sensed by B cells) [98,99] (F), but other receptors and ligands, depicted in (E) as R and L, respectively, might also be involved depending on the infected cell type, thus driving the switch to producing afucosylated IgG [100]. Abbreviations: CpG, CpG-rich DNA; ECM, extracellular matrix; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; TCR, T cell receptor; TGF, transforming growth factor.