Figure 3.
Lineage tracing of P2C-1F11 in the P#2 repertoires across the SARS-CoV-2 infection
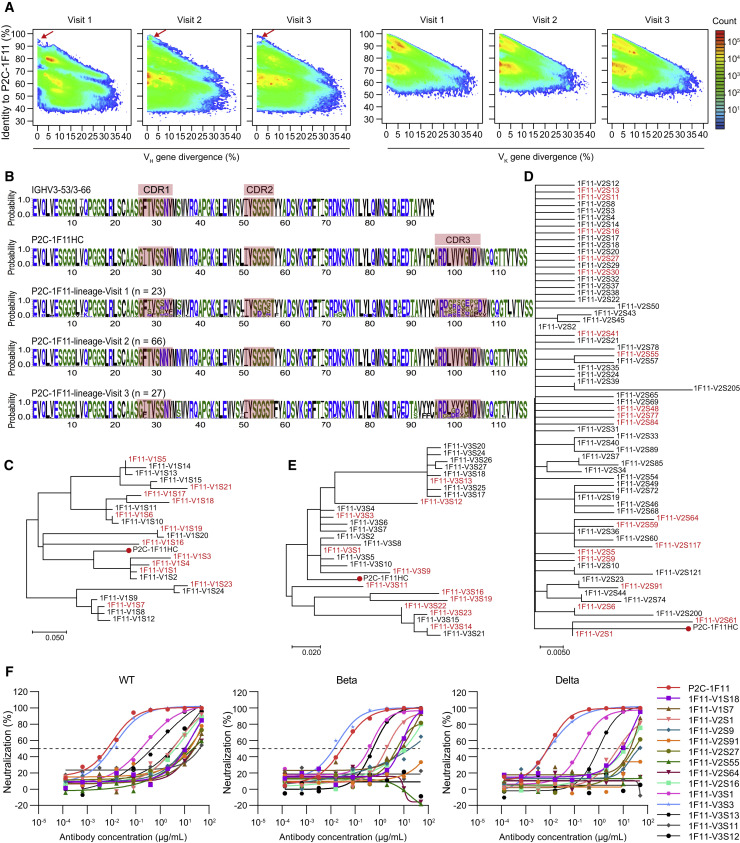
(A) Identity-divergence two-dimensional (2D) plots of heavy (left panel) and light (right panel) chain repertoires of P#2 at time points visit 1, visit 2, and visit 3. The x axis indicates the sequence divergence from the putative germline gene, and the y axis indicates their identity with respect to the P2C-1F11 heavy or κ chain. Color coding denotes the density of the sequence.
(B) Sequence logo of the P2C-1F11 lineage heavy chains at visit 1 (n = 23), visit 2 (n = 66), and visit 3 (n = 27) with their CDRs highlighted.
(C–E) Phylogenetic analysis of the heavy-chain sequences of P2C-1F11 lineage antibodies at (C) visit 1, (D) visit 2, and (E) visit 3. The maximum-likelihood trees were constructed on the basis of the amino acid sequences of selected antibodies. The synthesized heavy chains paired with the P2C-1F11 light chain for being functionally tested are highlighted in red, and branches of P2C-1F11 are marked with red dots.
(F) Neutralization of representative P2C-1F11 lineage antibodies against WT SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus and other variants (Beta and Delta). The P2C-1F11 lineage antibodies consisting of identified heavy chains and the P2C-1F11 light chain were synthesized and tested, with P2C-1F11 as the positive control. The curves are representatives of at least two independent experiments with similar results. A cutoff value of 50% is indicated by a horizontal dashed line.
See also Table S4.