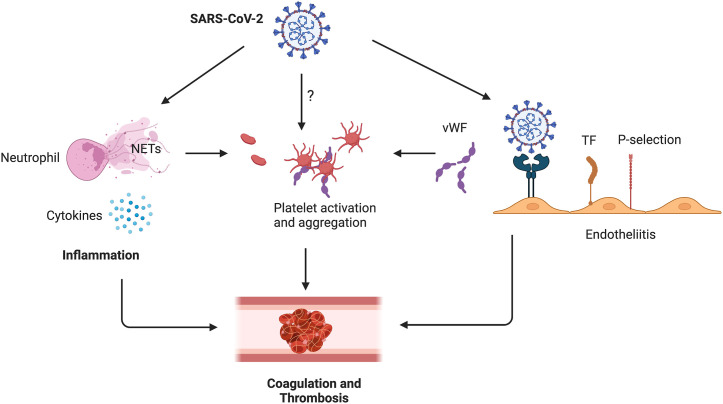
Fig. 1.
Formation of CAC in COVID-19 patients. SARS-CoV-2 infection will cause neutrophil activation and NET release, resulting in pathological prothrombotic environment. Pro-inflammatory cytokines can activate neutrophils and endothelial cells, which will further stimulate thrombosis. SARS-CoV-2 might be able to interact with platelets directly, leading to platelet activation and thrombosis. SARS-CoV-2 binding to ACE2 on endothelial cells causes endotheliitis, shifting the vascular equilibrium towards a procoagulant state.