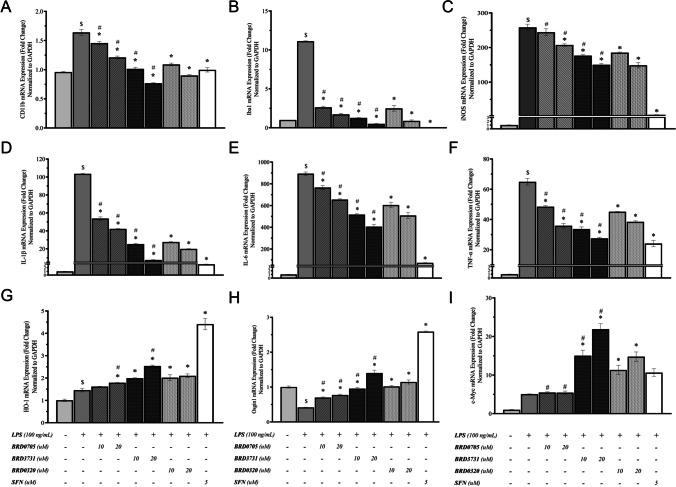
Fig. 5.
Effect of GSK-3 inhibitors on the mRNA expression of microglial activation, pro-inflammatory markers, Nrf2-driven ARE genes, and β-catenin − transcribed c-Myc in LPS-stimulated SIM-A9 cells. Target mRNA expression was quantified by real-time qPCR and normalized to GAPDH. All compounds show a dose-dependent decrease of the LPS-triggered upregulation of the microglial activation markers CD11b (a) and Iba1 (b), iNOS (c), and the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β (d), IL-6 (e), and TNF-α (f). All GSK3 inhibitor treatments — except for BRD0705 (GSK3α inhibitor) at 10 μM — show a statistically significant upregulation of the Nrf2-driven ARE gene HO-1 (a) and all treatments — without exceptions — correlate with a rise in Osgin1 mRNA levels (b). BRD3731 (GSK3β inhibitor) displays the greatest Nrf2-inducing activity after the positive control (SFN, 5 μM), followed by BRD0320 (GSK3α/β inhibitor), then BRD0705 (GSK3α inhibitor). Only BRD3731 (GSK3β inhibitor) and BRD0320 (GSK3α/β inhibitor) show a statistically significant augmentation of c-Myc transcription. BRD3731 (GSK3β inhibitor) displays the most β-catenin − inducing activity followed by BRD0320 (GSK3α/β inhibitor). BRD0705 (GSK3α inhibitor) does not induce any considerable change in c-Myc expression beyond that which is already occasioned by LPS alone. Data is expressed as means ± SEM. Group comparisons were drawn using one-way ANOVA, followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test; *P-value < 0.05 (relative to the LPS-stimulated group); $P-value < 0.05 (relative to negative [untreated] controls); #P-value < 0.05 (BRD0705 at any given concentration relative to BRD3731 at the corresponding concentration)