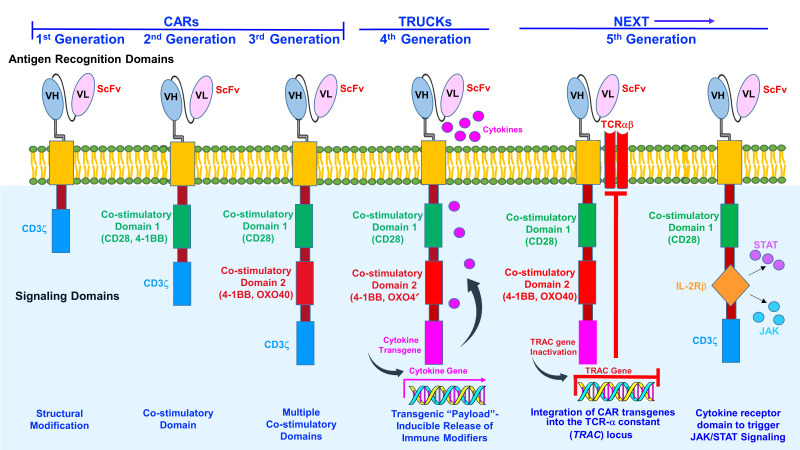
Figure 1.
Generations of CAR T-cells. The first-generation CAR T-cells consisted of an intracellular CD3 ζ- chain or FcϵRIγ domain. However, first-generation CAR T-cells did not generate sufficient IL-2 and exogenous IL-2 supplementation was required. In the second- generation, additional signaling domains comprised of T-cell cytokine and costimulatory receptors CAR T-cells were included in the design. Co-stimulatory domains promote IL-2 synthesis to enhance T-cell activation and reduce apoptosis. Third-generation CAR T-cells contain an antigen recognition domain, hinge, membrane-spanning region and a cytoplasmic domain. Third-generation CAR T-cells consist of two co-stimulatory signaling units, e.g., CD28 (B7), CD137 (4-1BB), CD134, (OX40), DAP10, as well as a CD3ζ or FcϵRIγ domain. Third-generation CARs promote cytokine secretion to increase T-cell proliferation and survival. Fourth-generation CARs T-cells (TRUCKs) store transgenic cytokine and release it when induced to attract innate immune cells. Some constructs also incorporate a suicide gene, e.g., Caspase-9, to rapidly withdraw CAR T-cells once anti-tumor effects are reached. Two examples of newly emerging fifth (next)-generation CAR T cells are shown. Next-generation (fifth-generation) CAR T-cells integrate CAR transgenes into the TCR-α constant (TRAC) locus. CAR can be directed to the TRAC locus, resulting in uniform CAR expression, reduced tonic signaling, decreased exhaustion and increased antitumor efficacy and gives the added benefit of producing a potential universal product. To induce JAK-STAT pathway activation in CAR-T cells in an antigen-dependent manner, the full-length or truncated cytoplasmic domain of a membrane receptor, e.g., IL-2 receptor-β can be incorporated between the cytoplasmic domains of CD28 and CD3z. The cytokine receptor domain triggers JAK/STAT signaling to promote proliferative capacity and functional activity.