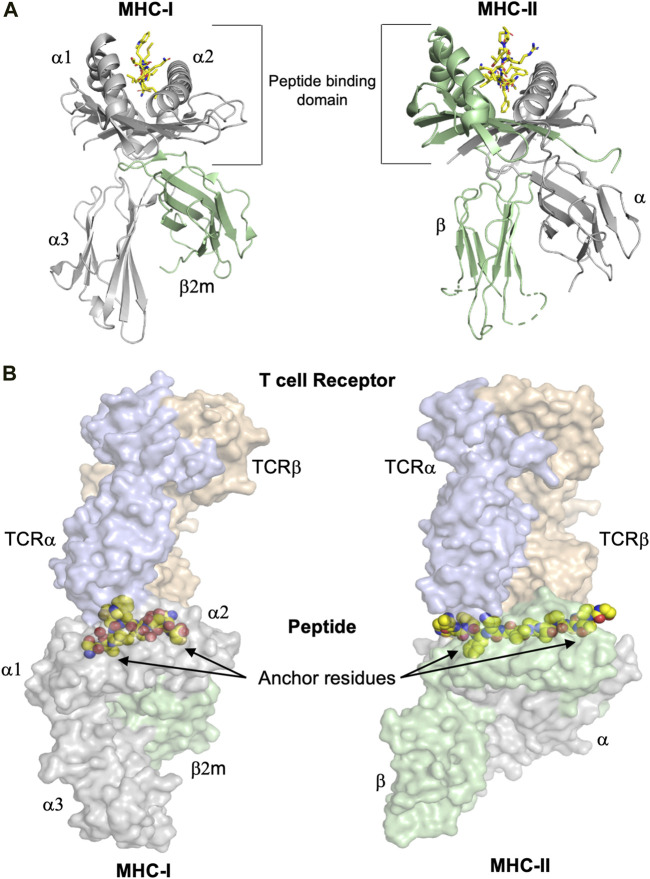
FIGURE 1.
The overall structures of MHC-I and MHC-II complexes are similar. (A) Despite the similarity of their overall three dimensional folds, there are some significant differences between MHC-I and MHC-II molecules. Left panel: The polymorphic MHC-I heavy chain, colored in grey, comprises the peptide binding domain (PBD or α1-α2 domain) and an additional Ig-like domain denominated α3. Furthermore, the almost invariable Ig-like β2-microglobulin (β2m) domain, colored in green, binds non-covalently between the α1-α2 and α3 entities, stabilizing the overall structure of MHC-I/peptide complexes (pMHC). The peptide is colored in yellow. Right panel: MHC-II molecules consist of the two polymorphic α and β chains (in grey and green, respectively), each one comprising half of the PBD and each one with an additional Ig domain that separates the PBD from the cell membrane. The peptide is colored in yellow. (B) T cell receptors bind on the top of pMHC molecules, interacting with both the presented peptides and the MHC chains. The surfaces of both TCR and pMHC are semitransparent. Left panel: The α and β chains of the MHC-I-restricted TCR are colored light blue and orange, respectively, while the surfaces of the heavy chain and β2m are in light violet and light green, respectively. The side chains of the presented peptide are represented by yellow spheres. Nitrogen and oxygen atoms are in blue and red, respectively. Classical examples of canonical peptide anchor residues are indicated by arrows, with their side chains buried within specific MHC pockets. The N- and C-termini of MHC-I peptide-binding clefts are closed, restricting most often the length of the bound peptides to 8–10 amino acids. Right panel: The α and β chains of the MHC-II-restricted TCR are in light blue and orange, respectively. The three dimensional structures of the ternary complexes derveal that MHC-II-restricted TCRs most often bind very similarly to their cognate pMHC-II complexes compared to MHC-I-restricted TCRs. In contrast to a majority of MHC-I-restricted peptides, the flanking residues of most MHC-II-restricted epitopes are protruding our from both the N- and C-termini of the MHC-II cleft and are more solvent accessible. All figures were created using PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.3.0, Schrödinger, LLC). All figures were created using the TCR/pMHC ternary structures determined in 2BNR.pdb and 1ZGL.pdb.