FIGURE 4.
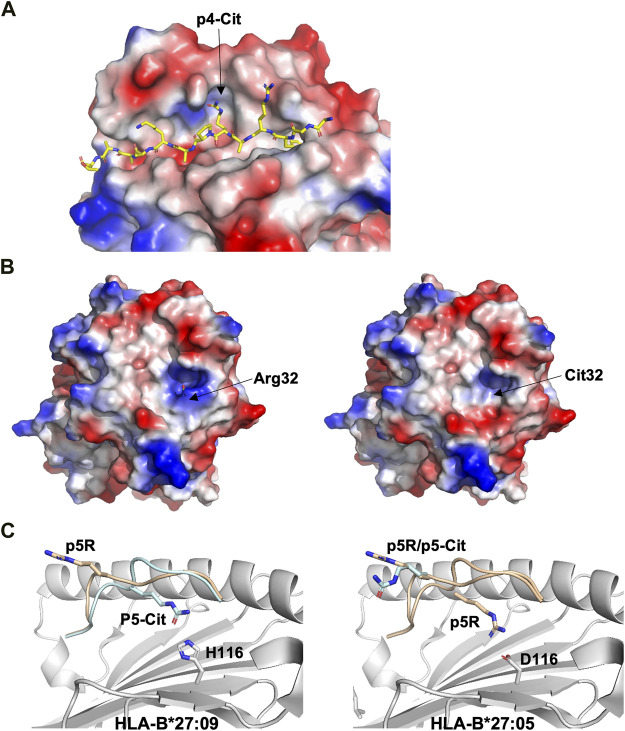
Citrullination may allow binding of neoantigens to MHC, modify surface electrostatics and alter the conformations of presented peptides (A). The side chain of a citrullinated arginine residue can bind to the slightly positively charged pocket 4 in HLA-DRB1*04:01 while the side chain of an arginine residue will be repelled, as exemplified here by the crystal structure of the citrullinated fibrinogen peptide (6BIL.pdb) (Ting et al., 2018). The peptide, colored in yellow, binds to the cleft of HLA-DRB1*04:01 with the N- and C-termini extending to the left and right of the peptide binding cleft, respectively. The side chain of the citrullinated residue at p4 is indicated, binding to the slightly positively charged pocket 4 in HLA-DRB1*04:01. The surface of HLA-DRB1*04:01 is colored according to surface electrostatics, with negatively and positively charged regions in red and blue, respectively (B). Citrullination of peptides may result in modification of the pMHC surface electrostatic potential, as exemplified by the surfaces of HLA-DRB1*04:01 in complex with the wild-type enolase-derived epitope eno26-40 (5LAX.pdb, left) or with the citrullinated PTM variant (5JLZ.pdb, right) (Gerstner et al., 2016). Here, citrullination reduces significantly the size of the positively charged region, possibly leading to the selection of alternative TCRs. Both structures are presented from the TCR view (C). The conformation of the self-peptide VIRP400-408 depends on the MHC-I allele it binds to. Wild-type VIRP400-408 binds to HLA-B*27:09 with the side chain of the arginine residue p5R protruding towards the solvent and a presumptive TCR (1OGT.pdb, colored in light orange, left panel). Citrullination of p5R in VIRP400-408 modifies significantly the conformation of the PTM peptide compared to wild-type VIRP400-408. The side chain of p5R in the citrullinated VIRP400-408 dives instead within the cleft of B*27:09 forming hydrogen bonds with the side chain of H116 (3B3I.pdb, colored in blue, left panel). VIRP400-408 takes two different conformations when binding to HLA-B*27:05, one similar to the one described for the HLA-B*27:09/VIRP400-408 complex and one diametrically different in which the peptide flips and the side chain of p5R forms hydrogen bonds with the side chain of the HLA-B*27:05 aspartate residue D116 (1OGT.pdb, colored in light orange, right panel). Importantly, citrullination of p5R forces the formation of only one peptide conformation in which the side chain of the citrulline residue protrudes towards the solvent (3B6S.pdb, colored in light blue, right panel) (Beltrami et al., 2008).