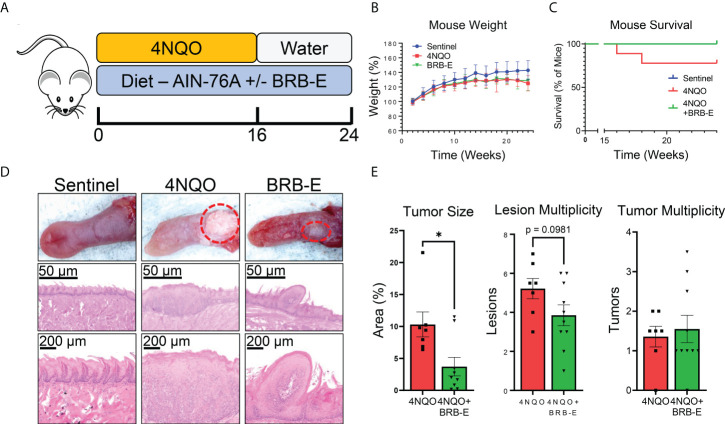
Figure 1.
Black raspberry extract (BRB-E) inhibits HNSCC carcinogenesis in a carcinogenesis model of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. (A) Study design of the 4NQO carcinogen-induced murine model of HNSCC and dietary BRB-E chemoprevention. (B) Percent weights of mice over time throughout the duration of the HNSCC cancer chemoprevention study. Data are represented as the percent weight over time relative to the initial weight of the mice. (C) Kaplan–Meier survival probability of non-carcinogen-induced mice (sentinel), and carcinogen-induced mice fed the control AIN76 diet (4NQO) or the BRB-E-supplemented diet (4NQO+BRB-E). (D) Representative images of tongues taken from mice in each group and images of representative H&E-stained tongues from each group at 50× and 200× total magnification. (E) Total percent of tongue surface area bearing tumors determined by image analysis. Total lesion and tumor count on each tongue taken from mice at terminal sacrifice. Each point represents the average of counts taken by three researchers trained to identify lesions or tumors taken in a blinded manner. *p-value < 0.05; for comparisons of BRB-E treatment groups to 4NQO-exposed control diet group using Student’s t-test. Sentinel (n = 10), 4NQO (n = 7), and BRB-E (n = 10).