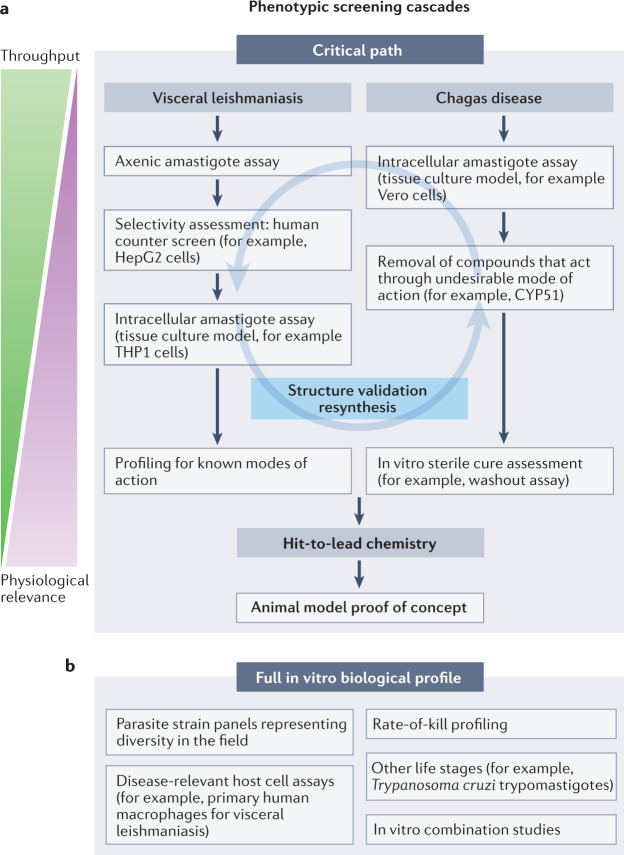
Fig. 4. Representative screening cascades for drugs to treat visceral leishmaniasis and Chagas disease.
a | Key assays for a phenotypic hit discovery programme are shown. For visceral leishmaniasis, the main purpose is to quickly identify compounds that are active in intracellular models, as such compounds have a high chance of demonstrating proof of concept in animal models (provided they have appropriate pharmacokinetics). High-throughput screening for visceral leishmaniasis is typically performed with axenically grown parasites, in particular axenic amastigotes. Initial screening can also be conducted in intracellular models, if high-throughput assays are available, or for smaller compound libraries. Following axenic assays, compounds that are non-selective regarding human cells are removed, and compounds of interest progress to intracellular assays. At this point, any compounds with suitable activity should be validated through structure and purity determination and/or resynthesis. Confirmed active compounds are next subjected to analysis of known modes of action, in particular to identify compounds that have a mode of action that is already being tested in the clinic. For Chagas disease, the cascade needs to quickly remove compounds with undesirable modes of action and identify compounds that can achieve complete cure. Hits are usually identified in high-throughput intracellular systems, as there are no suitable axenic models. Typically, a large fraction of hits act through undesirable modes of action such as CYP51, and screening to remove these is done early in the cascade. Remaining compounds of interest should at this stage be validated for structure and purity. For Chagas disease, it is thought that compounds that can kill all parasites have the highest chance of success in the clinic. To assess ability to achieve sterile cure, compound washout and parasite outgrowth assays are applied. For both diseases, validated hits next progress to hit-to-lead chemistry, with the main aim to achieve proof-of-concept efficacy in a suitable animal model of disease. b | For key compounds in each series, a full biological profile should be determined. This includes determination of potency against multiple relevant strains and host cells, determination of the rate of kill of compounds and profiling against different life stages. In addition, to understand potential for future combination treatments, key series can be profiled in combination experiments.