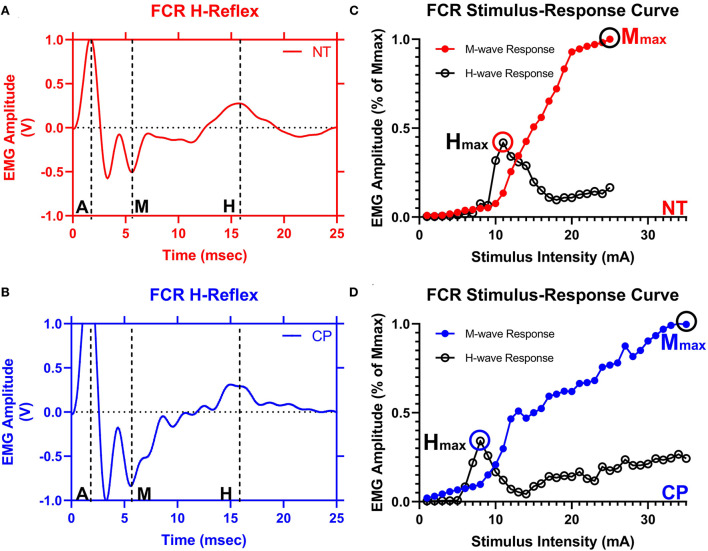
Figure 2.
The flexor carpi radialis H-reflex is reduced in adults with cerebral palsy. Averaged H-waves and M-waves across stimulus intensities from an exemplary neurotypical (NT) adult (A) and an adult with cerebral palsy (CP) (B) are shown. The exemplary subjects were chosen based on their similarity to the means of the respective groups. EMG amplitude from the flexor carpi radialis (FCR) muscle is shown on the y-axis and time (ms) is denoted on the x-axis, with 0 ms defined as the onset of the stimulus artifact. As can be discerned in (A,B), there is an M-wave response around 4 to 5 ms after the stimulus artifact and an H-wave response around 14 to 16 ms after the stimulus. M, M-wave; H, H-wave; A, stimulus artifact. (C,D) show M-wave (closed circle) and H-reflex (open circle) recruitment curves obtained with median nerve stimulation from the same exemplary NT control and adult with CP. Response peak-to-peak amplitudes were normalized to the maximal M-wave response (Mmax) and shown on the y-axis and stimulus intensity (in mA of current) is denoted on the x-axis. As depicted, the H-max was lower for the adult with CP when compared with the NT adult.