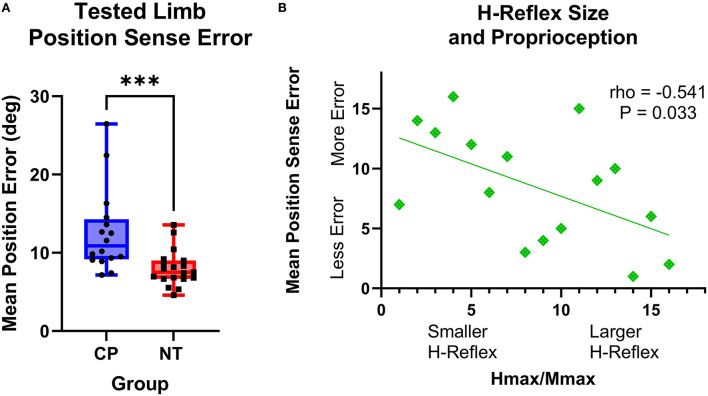
Figure 5.
The H-reflex size is related to position sense error in adults with cerebral palsy. (A) Box-and-whisker plots of the group mean position errors for the adults with cerebral palsy (CP) and neurotypical (NT) adult controls. As shown, the average position sense errors were significantly greater for the adults with CP. ***Indicates P < 0.001. (B) Rank-order correlation between the mean position sense error and H-reflex H:M ratios at rest for the adults with CP. As shown, there was a significant negative correlation between the strength of the H-reflex size (H:M ratio) and the participant's mean position sense error (rho = −0.541; P = 0.033). This implies that adults with CP that had a lower H-reflex at rest also tended to have greater errors in their perception of wrist joint position.