Figure 4.
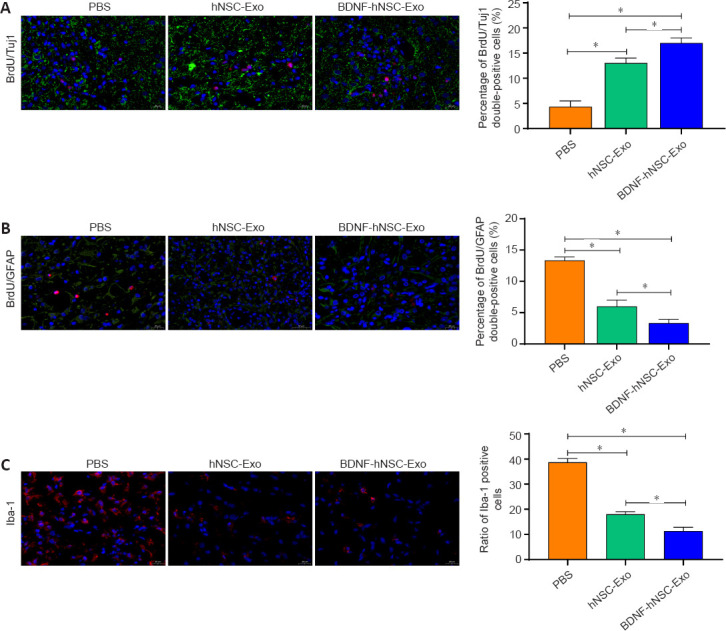
BDNF-hNSC-Exo inhibit neuroinflammation and promote neurogenesis in the peri-infarct zone of rats.
(A) Immunofluorescence double-labeling demonstrated that more functional neurons in the peri-infarct area were generated in the BDNF-hNSC-Exo and hNSC-Exo groups than in the PBS group. BrdU (red) co-localized with Tuj1 (green). Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm. n = 5 rats/group. (B) Double immunofluorescence staining showed that in the BDNF-hNSC-Exo group, the proportion of BrdU/GFAP double-positive cells in the peri-infarct area was lower than that in the hNSC-Exo group and the PBS group on day 28 after treatment. BrdU (red) co-localized with GFAP (green). Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm. n = 5 rats/group. (C) Immunofluorescence showed that BDNF-hNSC-Exo significantly reduced the expression of Iba1 (red), indicating reduced neuroinflammation. Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm. n = 5 rats/group. All data are shown as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BrdU: bromodeoxyuridine; Exo: exosomes; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; hNSC: human neural stem cell; Iba1: induction of brown adipocytes 1; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; Tuj1: β-tubulin.
