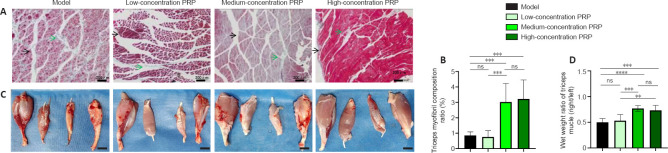
Figure 4.
Effects of PRP on tricep recovery in rabbits with sciatic nerve injury.
(A) Masson’s trichrome staining of triceps. Black arrows indicate muscle fibers, and green arrows indicate collagen fibers. The tricep myofibril composition ratios in the medium- and high-concentration PRP groups were significantly higher than those in the model and low-concentration PRP groups. Scale bars: 200 μm. (B) Quantitative results for the tricep myofibril composition ratios. (C) Bilateral tricep and tibialis anterior muscles. The injured side is on the right. The wet weight ratios of the triceps were significantly higher in the medium- and high-concentration PRP groups than those in the model and low-concentration PRP groups. Scale bars: 2 cm. (D) Quantitative results for wet tricep weights. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 7). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 (Tukey’s multiple comparison test). ns: Not significant; PRP: platelet-rich plasma.