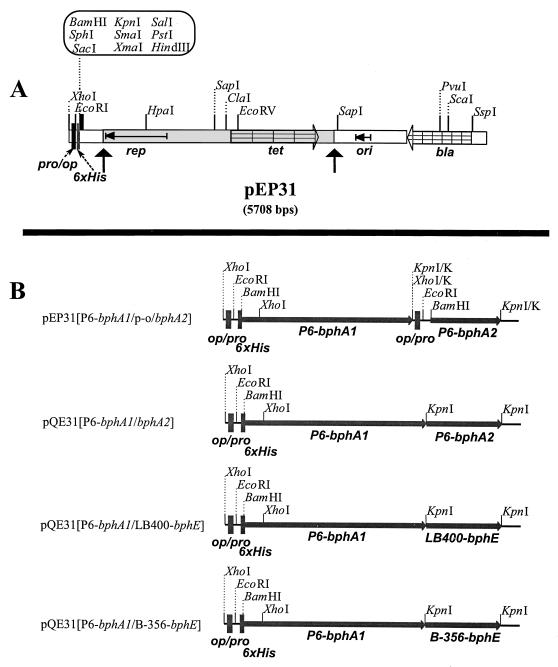
FIG. 1.
(A) Linear map of the E. coli-Pseudomonas shuttle vector pEP31 designed to produce ht-proteins. Only selected restriction sites are shown. The grey and white areas derive from pUCP26 and pQE31, respectively. rep, origin of replication in Pseudomonas; tet, tetracycline resistance; bla, ampicillin resistance; ori, ColE1 origin of replication; pro/op, pQE31 promoter-operator; 6xHis, the six-histidine-tagged fusion gene. The map of pEP51 is identical to that of pEP31 except for the absence of the six-histidine-tagged fusion gene. (B) Constructs used to produce P6 ht-ISPBPH and chimeras derived from it. All constructs except pEP31[P6-bphA1/p-o/bphA2] were made in pQE31, and the cloned DNA fragment was transferred to pEP31 when needed. Details of the strategies used to construct these plasmids are given in Materials and Methods. Only the restriction sites important for the cloning strategies are shown. KpnI/K and XhoI/K indicate sites that were made blunt ended with the Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I, resulting in their loss in the final construct.