Figure 1. Ubiquitin-Dependent and -Independent “Segregase” Activity of p97.
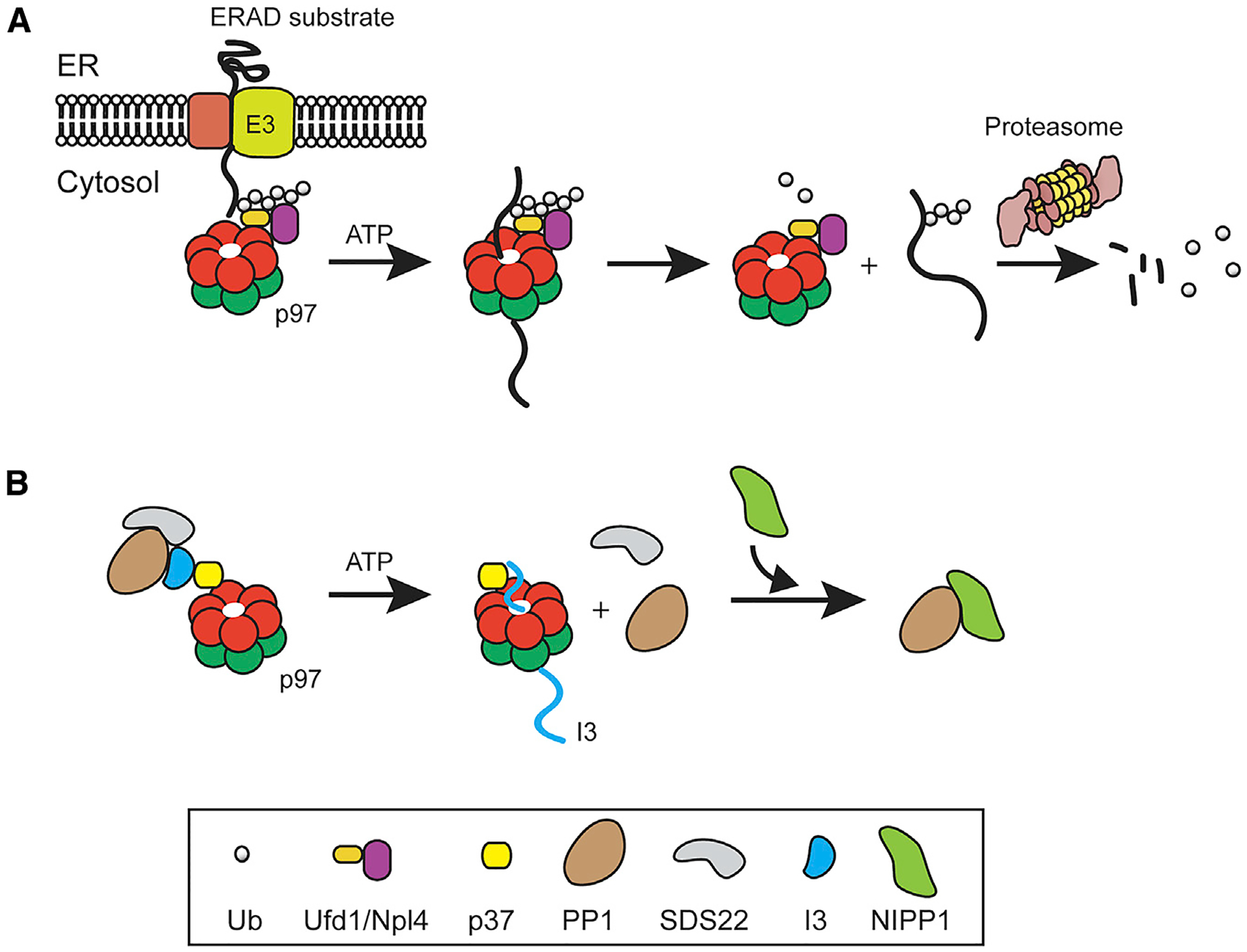
(A) In the ERAD pathway, substrates ubiquitinated during retrotranslocation by ER-associated ubiquitin ligase (E3) are recognized by the heterodimeric adaptor Ufd1-Npl4, which activates p97 to extract substrate from the ER membrane. p97 hydrolyzes ATP to move substrate through its central channel, thereby unfolding the substrate for proteasome degradation.
(B) In PP1 biogenesis, p97 associates with I3 in the PP1-SDS22-I3 complex via a SEP adaptor (e.g., p37). It then uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to translocate and unfold I3, which results in the disassembly of the inhibitory PP1 complex and subsequent binding of a substrate-specific cofactor (e.g., NIPP1) to PP1.
