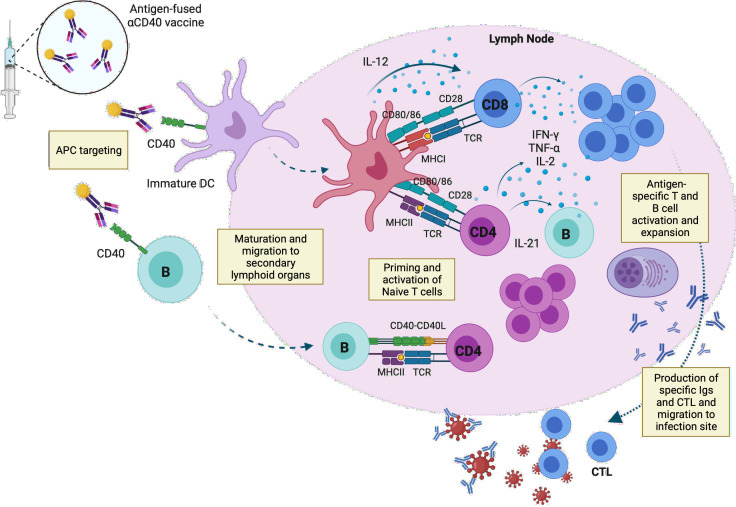
Figure 2.
Capture of the anti-CD40 vaccine by APCs and activation of T- and B-cell responses in the draining lymph node. Targeted vaccines recognize CD40 molecules expressed on the surface of immature DCs and B-cells. The vaccine induces the maturation and migration of the immune cells to secondary lymphoid organs, where they present the peptides to naïve T-cells through MHC-I and -II complexes. Mature DC release IL-12, which stimulates the differentiation and expansion of T-cells, which in turn release pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, TNFα or IL-2, promoting the activation of cytotoxic T-cells. B-cells can also present the antigen to naïve CD4+ T-cells through CD40-CD40 ligand, inducing maturation and proliferation of antigen specific T-cells, which trigger B-cell maturation by IL-21. Antigen specific antibodies and T-cells migrate to the infection site to neutralize the virus and face the pathogen. APC, antigen-presenting cells; IL, interleukin; CTL, Cytotoxic T lymphocyte; TCR, T-cell receptor. This image was created with BioRender software.