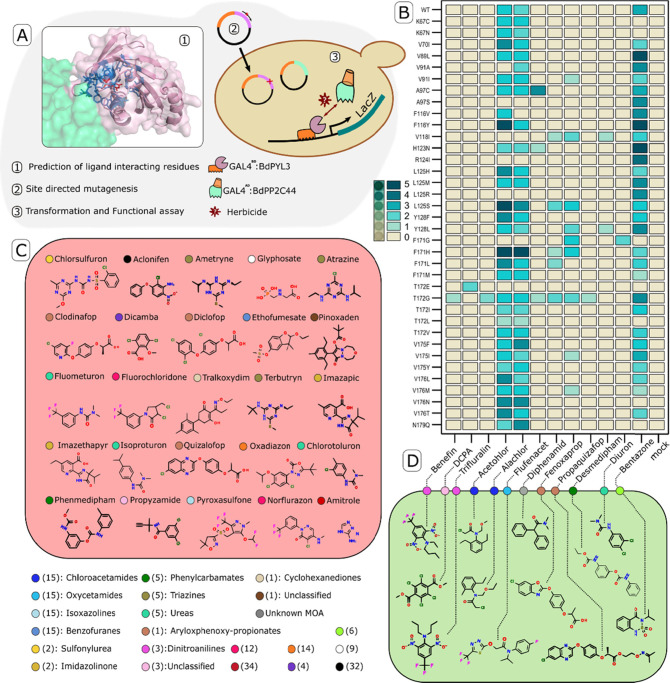
Figure 1.
Chemical yeast two-hybrid screen of a BdPYL3-mutant panel. (A) Solved structure of a receptor/ABA/PP2C complex (AtPYL2, ABA, and AtHAB1 in pink, red, and green, respectively) was used to predict 25 ligand cavity lining residues (<5 Å from ABA, highlighted in blue).15 A collection of 475 pBD-GAL4 plasmids carrying all possible substitutions at these positions was created by site-targeted mutagenesis and transformed separately into a pACT2-BdPP2C44-harboring Y2H strain (Y190). All lines were challenged with each herbicide and tested for induced PYL-PP2C interaction by LacZ activity assay. Plates were photographed under consistent illumination, and staining intensity was assessed manually according to a fixed 0–5 intensity ladder. (B) A partial report of this screen, containing all ″hits″ is provided in a heat-map format, with each row specifying a variant and each column representing a different herbicide. Chemical structures of compounds, for which induced receptor variants were or were not identified, are shown in green or red rectangles, respectively (C, D). Color-coded circles assign herbicides to different groups according to HRAC classification, with mode-of-action (MOA) classes indicated in parentheses. Chemical families within MOA classes are also specified if more than one family was represented in the screen. Class 1 compounds (acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors) were tested in their pro-herbicide form—see Table S1 for more details.