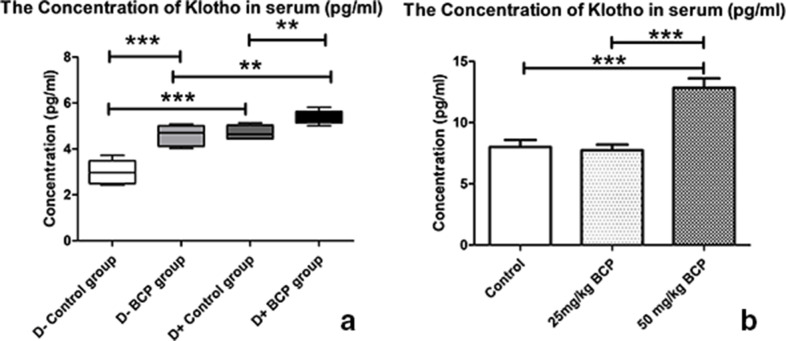
Fig. 5.
Detection of klotho in the serum of mice fed on vitamin D-containing and vitamin D-deficient diets that were treated with ß-caryophyllene (BCP) or with propylene glycol control. Whole blood was collected from mice, the serum fraction was isolated by centrifugation, sera from individuals in each group were pooled, and the relative levels of klotho were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). a) The effect of vitamin D and BCP treatment on serum levels of klotho. b) The effect of different concentrations of BCP treatment on levels of klotho in serum. Three groups of mice (n = 5/group) were fed on a vitamin D-sufficient diet for six weeks. For the last two weeks, they were treated by oral gavage for five days/week with propylene glycol control or with 25 mg/kg or 50 mg/kg BCP. Serum samples from each group were pooled and tested for the presence of klotho by ELISA. **p < 0.010; ***p < 0.001.