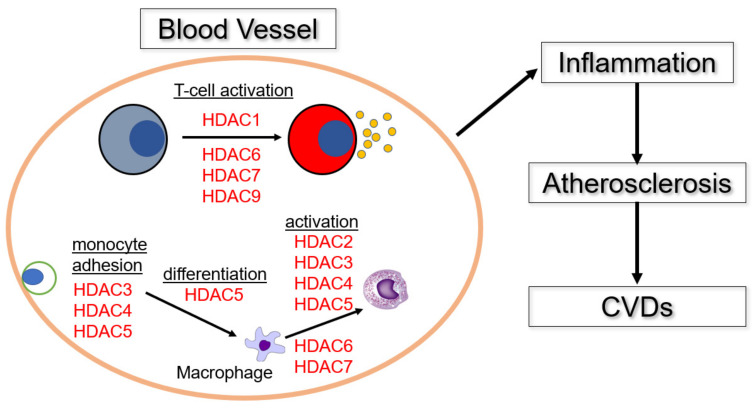
Figure 2.
The roles of HDACs in inflammation and development of CVDs. HDAC3, 4, and 5 promote migration and adhesion of monocytes to inflammatory sites [29,30,63,64], followed by induction of macrophage differentiation by HDAC5 [65]. The differentiated macrophages are activated by HDAC 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 [28,32,40,66,67]. And HDAC 6, 7, 8, and 9 promote T cell activation at inflammatory sites [53,54,68,69].