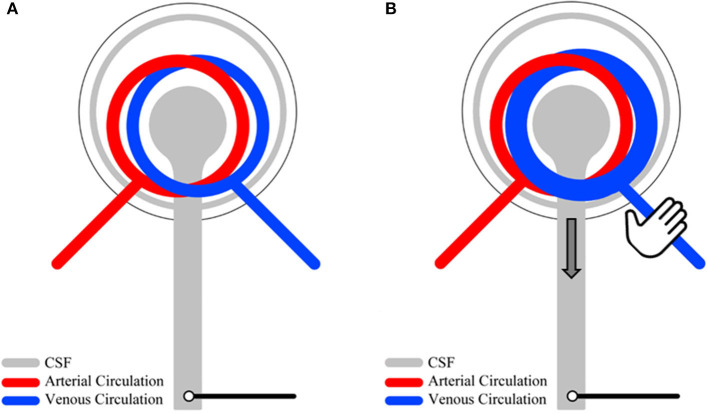
Figure 1.
An overview of CSF pressure (CSFP) dynamics. Under physiological resting-state conditions, lumbar cardiac-driven CSFP peak-to-trough amplitude (CSFPp) is a function of intracranial venous filling and arteriolar pulsations (A). During the Queckenstedt's test, intracranial venous filling is temporally increased due to reduced venous outflow, leading to an increased baseline CSFP and increased CSFPp (B).