Figure 2.
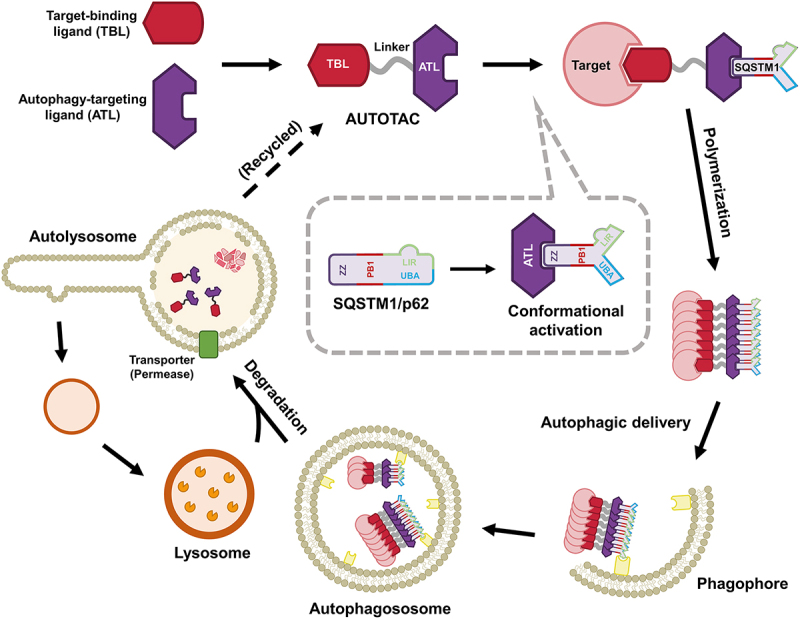
Graphical illustration of the AUTOTAC targeted protein degradation platform and its mechanism of action. The AUTOTAC platform employ bifunctional molecules composed of target-binding ligands (TBLs) linked to SQSTM1-binding autophagy-targeting ligands (ATLs). AUTOTACs simultaneously interact with the protein of interest and the ZZ domain of SQSTM1 via its TBL and ATL, respectively. When the ATL moiety interacts with the SQSTM1-ZZ domain in an Nt-Arg-mimicking manner, inactive SQSTM1 is conformationally and thus biologically activated for self-oligomerization, forming target-SQSTM1 oligomeric complexes near the site of autophagosome formation. Finally, AUTOTACs facilitate ubiquitin- and proteasome-independent degradation of the target-SQSTM1 complexes via macroautophagy and are then recycled from the lysosome for subsequent rounds of degradation, resulting in sustained efficacy.
