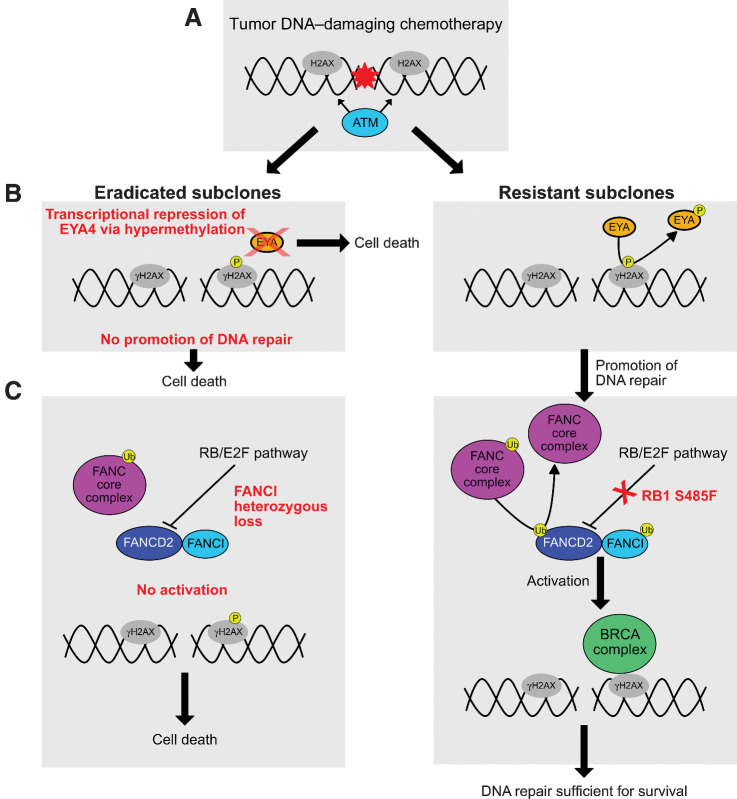
Figure 2.
DSER analysis in Case A34. A, Carboplatin and etoposide induce DNA double-strand breaks, causing histone H2AX to be targeted by ATM at its S139 phosphorylation site to form γH2AX. B, EYA proteins mediate the dephosphorylation of γH2AX at the Y142 residue to promote the repair response to DNA damage. A lack of EYA protein in the eradicated subclones and consequent lack of dephosphorylation enhances cell death relative to the resistant subclones. If EYA-mediated dephosphorylation occurs, the DNA repair response proceeds. C, Ubiquitination of the complex formed by FANCD2 and FANCI is required for activation of the BRCA DNA repair complex. If the ubiquitination is inhibited, this promotes cell death. Since the presence of FANCI is needed for FANCD2 ubiquitination, and compensatory increase in FANCD2 activity is known to occur in BRCA2-deficient tumors (12), absence (and/or reduced levels) of FANCI would likely lead to enhanced cell death in the face of DNA damaging chemotherapy. The RB/E2F pathway is implicated as a negative regulator of FANCD2 transcription. Deleterious RB1 S485F (present in all three resistant liver metastases) could lead to increased FANCD2 levels and enhanced DNA-repair response, leading to subclone survival during DNA-damaging chemotherapy.