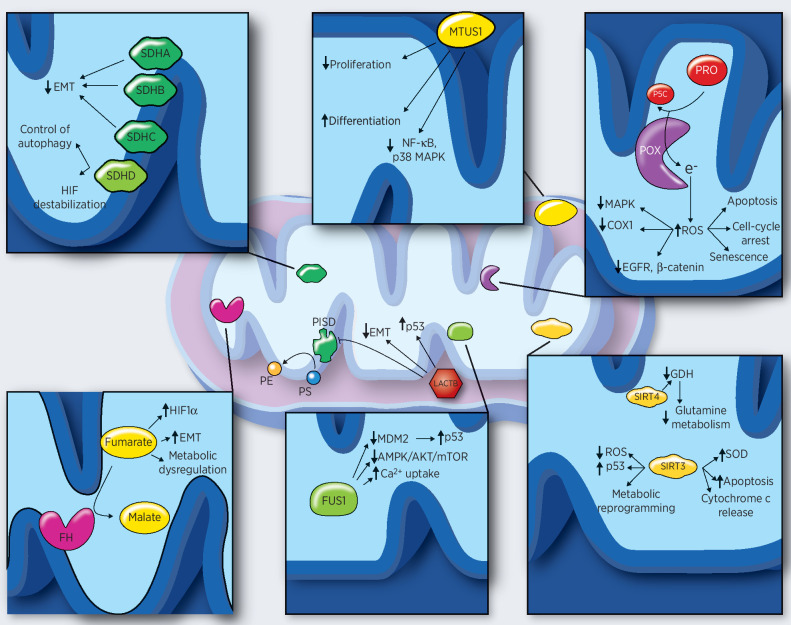
Figure 1.
Individual mitochondrial tumor suppressors and their main mechanisms of action. LACTB expression leads to stabilization of P53, downregulation of PISD and EMT, and induction of differentiation. SDHA, SDHB, and SDHC decrease EMT, whereas SDHD controls the autophagy and induces HIF1α destabilization. MTUS1 controls NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways and is able to induce differentiation and repress cancer cell proliferation. Increased ROS levels, due to the enzymatic activity of POX, impair MAPK, EGFR, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways; decrease COX1 levels; and induce apoptosis, cell-cycle arrest, and senescence. FH catalyzes the reaction from fumarate to malate. Accumulation of fumarate, due to FH inactivation, induces HIF1 stabilization, EMT, and metabolic dysregulation. FUS1 stabilizes p53 through MDM2, inhibits AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathways, and enhances Ca2+ uptake. SIRT3 activity leads to p53 stabilization decrease in ROS levels, metabolic reprogramming, apoptosis, and increase in SOD levels. SIRT4 downregulates the glutamine metabolism through GDH. GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; MDM2, mouse double minute 2; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; P5C, Δ1-pyroline-5-carboxylate; PISD, phosphatidylserine decarboxylase; PRO, proline; PS, phosphatidylserine; SOD, superoxide dismutase.