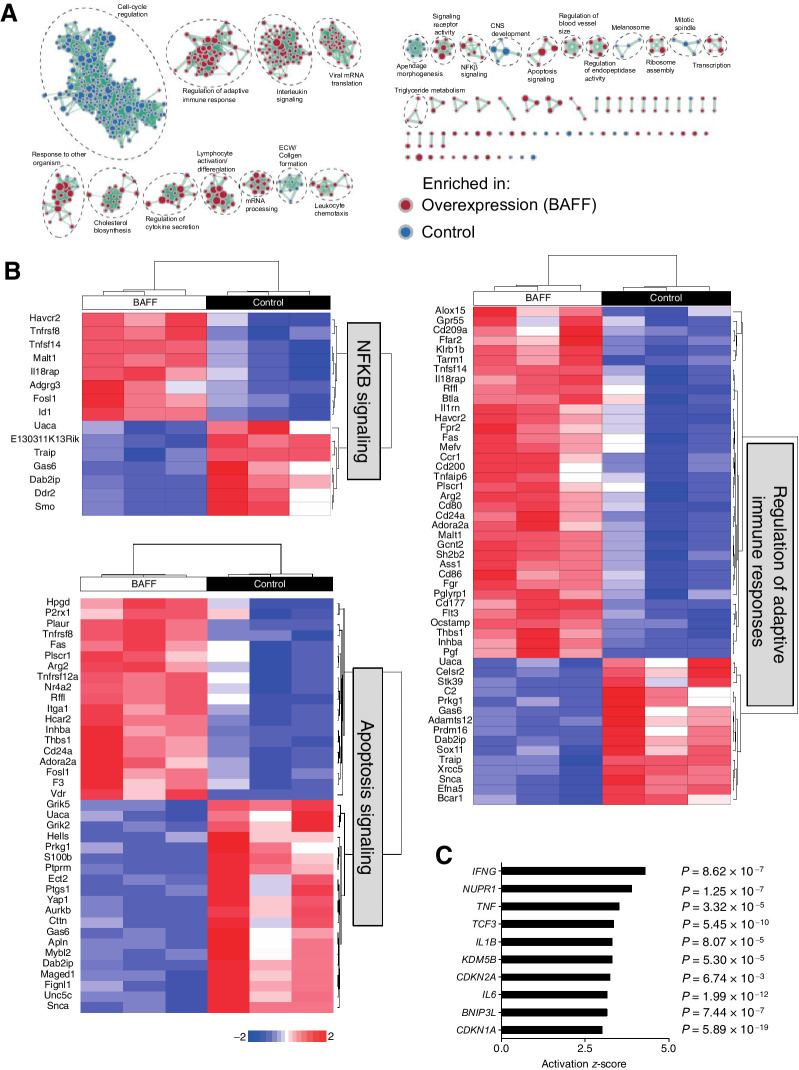
Figure 5.
BAFF induces differential gene expression in tumor-infiltrating monocytes. C57BL/6 mice were inoculated subcutaneously with 5 × 105 of BAFF-expressing or control cells. A, Thirteen days post-inoculation, monocytes were sorted from BAFF and control tumors, and analyzed using RNA-seq analysis for GSEA. B, Significant individual genes differentially regulated in regulation of adaptive immune responses, apoptosis, and NF-κB signaling pathways are shown as heatmaps. C, Top upstream regulators as assessed by IPA in monocytes harvested form BAFF-expressing tumors are shown (n = 3).