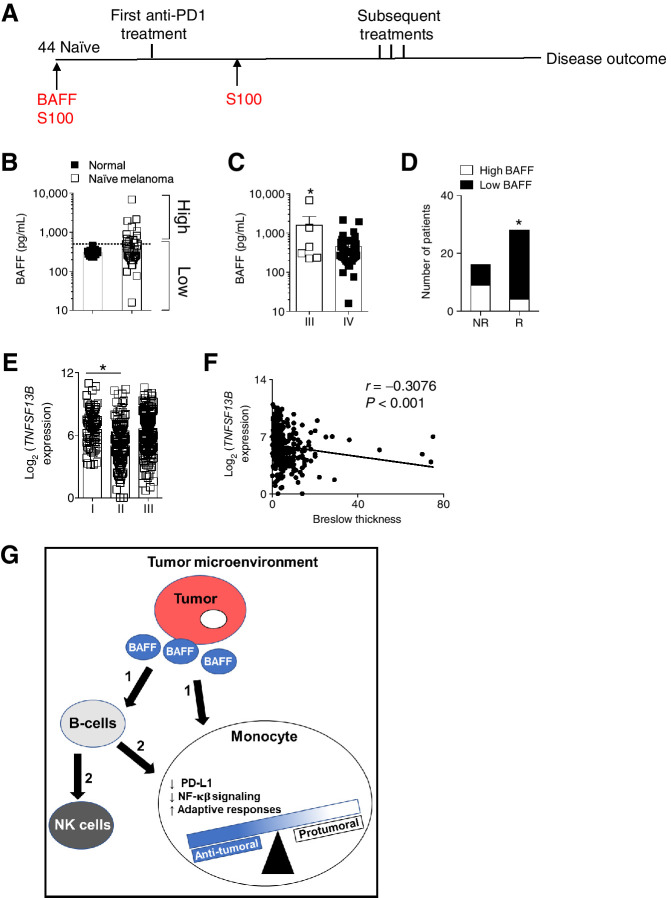
Figure 7.
BAFF serum levels affect response to immunotherapy. A, A schematic of the time line of sample collection (red) and treatment (black) of naïve melanoma patients is shown. BAFF plasma levels were assessed in healthy controls (n = 11) and naïve melanoma patients (n = 44). B, Patients were stratified according to their BAFF plasma levels into high and low groups. C, BAFF plasma levels of patients categorized according to tumor stage are shown. D, Best response to anti-PD-1 therapy was compared in the high and low BAFF naïve melanoma patients. E, Expression of tumoral BAFF mined from TCGA using the R2: Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform was grouped by melanoma stage. F, BAFF expression was correlated with Breslow thickness. G, A model proposing effects of intratumoral BAFF on the immune infiltrates in the TME is shown. It is proposed that tumoral BAFF directly (1) affects monocytes or indirectly (2) through other immune infiltrates, mainly B cells. Error bars in all experiments indicate SEM. *, P < 0.05 as determined by a Student t test (unpaired, two-tailed). A Fisher exact test was used to compare proportions of responders in the high and low BAFF groups.