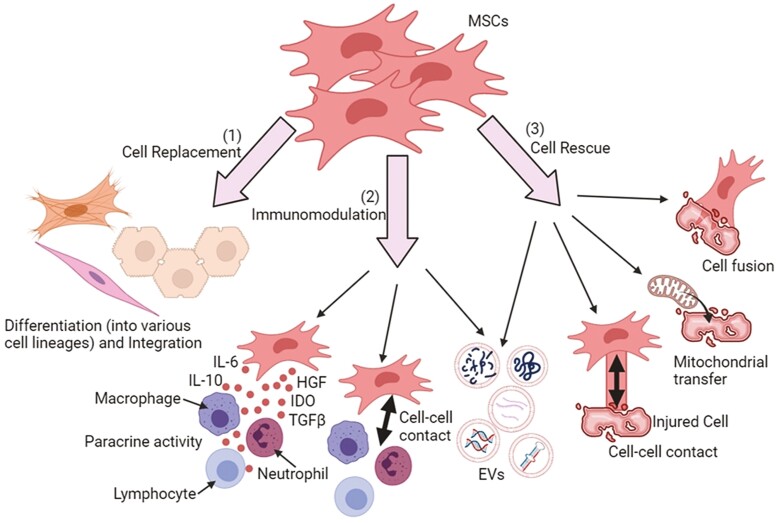
Figure 1.
Mechanisms underlying MSC-based therapy. (1) Cell replacement; MSCs can differentiate into various cell lineages and replace the damaged tissues. (2) Immunomodulation; MSCs can regulate immune responses through paracrine activity whereby secretome (ie, soluble factors and extracellular vesicles [EVs]) are released to exert immunomodulatory, pro-mitotic, pro-angiogenic, antiapoptotic, and antioxidative effects. (3) Cell rescue; MSCs can rescue or repair the damaged tissues through cell-cell contact, EV secretion, mitochondrial transfer, and cell fusion. All these biological activities lead to the transfer of cellular components to injured cells.
Abbreviations: IL-6, interleukin-6; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β, ATP, adenosine triphosphate.