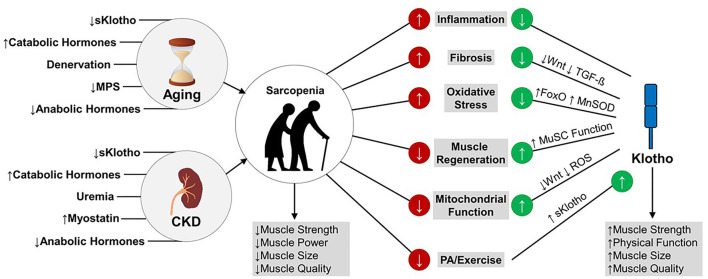
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of Klotho's effects on muscle function in aging and CKD. Age- and CKD-related declines in skeletal muscle strength, power, size, and quality lead to sarcopenia. These declines in muscle structure and function are partly driven by increased inflammation and oxidative stress, impaired muscle regeneration in favor of fibrosis, and impaired mitochondrial function. Emerging data suggest that enhancing Klotho levels may reverse sarcopenia by downregulating pro-fibrotic pathways, enhancing muscle satellite cell and mitochondrial function, and downregulating oxidative stress and inflammation. Accordingly, higher circulating levels of Klotho are associated with greater muscle strength and physical function, higher lean mass, and higher muscle quality. Klotho levels have been shown to increase in response to exercise. MPS, muscle protein synthesis; TGF-ß, Transforming Growth Factor-ß; FoxO, Forkhead box protein O; MnSOD, Manganese Superoxide Dismutase; MuSC, Muscle Satellite Cell; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; sKlotho, soluble Klotho; PA, Physical Activity.