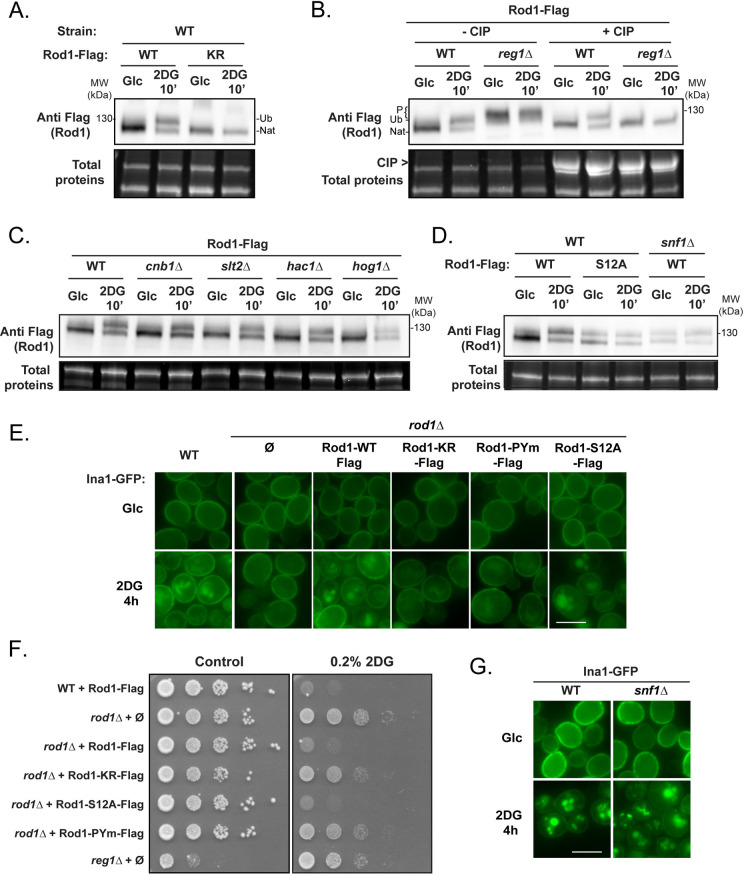
Fig 2. Following 2DG treatment, Rod1 is dephosphorylated in a PP1-dependent manner.
(A) Total protein extracts of WT cells expressing either Rod1-Flag or Rod1-KR-Flag were prepared before and after 2DG addition for 10’, and immunoblotted using an anti-Flag antibody. Ub: ubiquitylated Rod1, Nat: native Rod1. (B) Total protein extracts of WT or reg1Δ cells expressing Rod1-Flag were prepared before and after 2DG addition for 10’, and immunoblotted using an anti-Flag antibody. Samples were dephosphorylated by CIP where indicated. Ub: ubiquitylated Rod1, Nat: native Rod1, P: phosphorylated Rod1. (C) Total protein extracts of WT, cnb1Δ, slt2Δ, hac1Δ, or hog1Δ expressing Rod1-Flag were prepared before and after 2DG addition for 10’, and immunoblotted using an anti-Flag antibody. (D) Total protein extract of WT or snf1Δ cells expressing Rod1-Flag or Rod1-S12A-Flag were prepared before and after 2DG addition for 10’ and immunoblotted using an anti-Flag antibody. (E) WT or rod1Δ cells expressing the various ROD1-Flag constructs were grown in a glucose-containing medium and observed by fluorescence microscopy before and after 2DG treatment for 4h. Scale bar, 5 μm. (F) Serial dilutions of cultures of the indicated strains were spotted on SC medium or SC + 0.2% 2DG medium and grown for 4 days at 30°C. (G) WT or snf1Δ cells expressing Ina1-GFP were grown in a glucose-containing medium and observed by fluorescence microscopy before and after 2DG treatment for 4h. Scale bar, 5 μm.