Fig. 1.
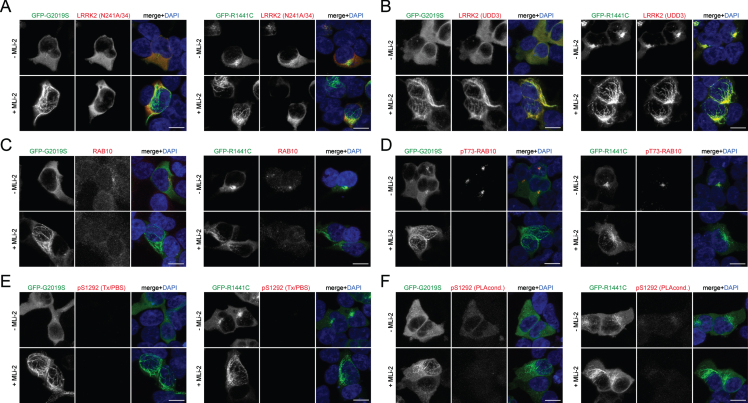
Immunocytochemistry in HEK293T cells overexpressing LRRK2. A) Example of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with either GFP-tagged G2019S (left) or R1441C (right) LRRK2, treated with or without MLi-2 (100 nM, 2 h) before immunocytochemistry as indicated, and stained with anti-LRRK2 antibody (N241A/34) and DAPI. Note that the N241A/34 LRRK2 antibody largely does not recognize LRRK2 when bound to microtubules (either R1441C LRRK2 or induced upon MLi-2 treatment). B) Same as in (A), but cells stained with anti-LRRK2 antibody (UDD3) and DAPI. Note that the UDD3 LRRK2 antibody recognizes LRRK2 also when bound to microtubules. C) Same as in (A), but cells stained with knockout-validated RAB10 (SAB5300028) antibody and DAPI. Note that weak staining is observed in transfected and non-transfected cells. A perinuclear accumulation of RAB10 is observed in cells transfected with pathogenic LRRK2 in the absence but not presence of MLi-2, as previously described [19]. D) Same as in (A), but cells stained with an anti-pT73-RAB10 antibody (ab241060) and DAPI. Note the perinuclear accumulation of phospho-RAB10 in pathogenic LRRK2-expressing cells, which is abolished upon treatment with MLi-2, as previously described. E) Same as in (A), but cells stained with pS1292-LRRK2 antibody and DAPI. No signal is observed in transfected cells when staining is performed using Triton-X100/PBS-containing buffer. F) Same as in (A), but cells stained with pS1292-LRRK2 antibody and DAPI. A hardly detectable signal is observed in transfected cells when staining is performed using proprietary PLA buffer conditions, and the signal is gone upon MLi-2 treatment. Scale bars, 10 μm. Experiments were performed a total of three times, with comparable results obtained in all cases.