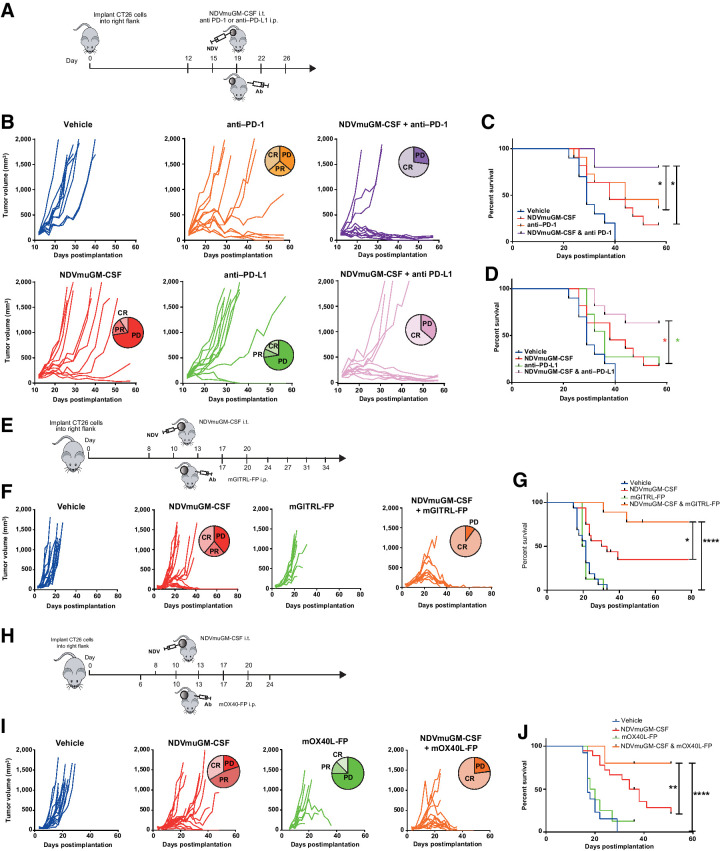
Figure 3.
Combination of NDV with immune checkpoint blockade or T-cell agonists in preclinical models. A, Representation of study design combining local NDVmuGM-CSF administration with antibodies to PD-1 or PD-L1 in the CT26 model. B, Spider plots showing tumor growth kinetics in individual animals in each group (n = 10 per group), data are representative of three separate experiments. C and D, Kaplan–Meier survival analyses of NDVmuGM-CSF plus C, anti–PD-1 or D, PD-L1 antibody combination therapy compared with monotherapies. E, Schematic representation of study design combining NDVmuGM-CSF administration with mGITRL-FP agonist in the CT26 model. F, Spider plots showing tumor growth kinetics of the individual animals in each group (n = 10 per group except NDVmuGM-CSF, n = 18). G, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of NDVmuGM-CSF plus mGITRL-FP agonist combination therapy compared with vehicle control and NDVmuGM-CSF and mGITRL-FP monotherapies. H, Schematic representation of study design combining local administration of NDVmuGM-CSF with mOX40L-FP agonist in CT26 model. I, Spider plots showing tumor growth kinetics of the individual animals in each group (n = 10 per group except NDVmuGM-CSF and NDVmuGM-CSF + OX40L-FP, n = 18). J, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of NDVmuGM-CSF plus mOX40L-FP agonist combination therapy compared with monotherapy. CR, complete response; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response. Significance in survival was assessed by log–rank (Mantel–Cox) test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.