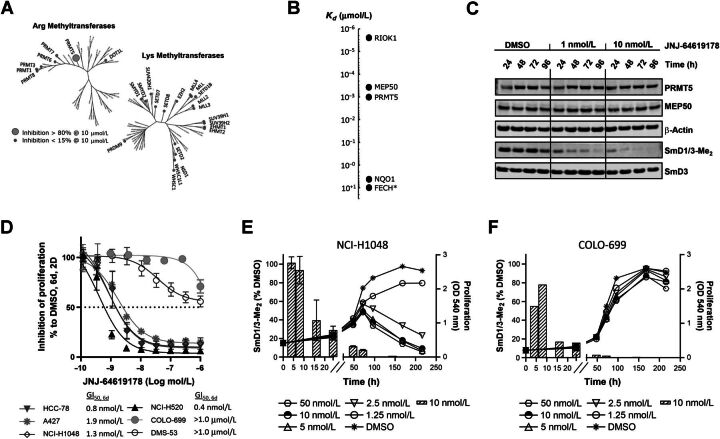
Figure 2.
JNJ-64619178 is a selective, time-dependent, and potent inhibitor of PRMT5 in cells and JNJ-64619178-mediated inhibition of symmetric arginine dimethylation of SmD1/3 proteins (SmD1/3-Me2) is a marker of target engagement, but not cancer cell sensitivity. A, Phylogenic trees depicting percentage (%) inhibition of recombinant human SAM arginine (Arg) and lysine (Lys) methyltransferases by JNJ-64619178 in vitro. Small gray circles indicate enzymes with <15% inhibition at 10 μmol/L JNJ-64619178, whereas the enlarged circle marks enzyme (in this case only PRMT5/MEP50 complex) with >80% inhibition at 10 μmol/L JNJ-64619178. B, Affinity (Kd value) of JNJ-64619178 binding to cellular proteins determined by competitive pull-down quantitative chemical proteomics. Extrapolated Kd value was assigned to FECH, marked with an asterix (*) due to partial competitive binding with JNJ-64619178. C, Cellular inhibition kinetics of Sym-Arg dimethylation of SmD1/3 proteins (SmD1/3-Me2) in NCI-H1048 cells at various time points following continued exposure of 0 (DMSO), 1 or 10 nmol/L of JNJ-64619178. D, Inhibition of human lung cancer cell line proliferation as measured by MTT after 6-day continuous treatment with JNJ-64619178 at multiple concentrations. GI50 values are listed on graph. GI50 values for COLO-699 and DMS-53 were set as the highest compound concentration tested (1.0 μmol/L), as 50% inhibition was not reached under the conditions tested. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD) from the mean. Exponentially growing (E) NCI-H1048 and (F) COLO-699 cancer cells were treated with DMSO or JNJ-64619178. Line graphs depict inhibition of cell proliferation (MTT assay, OD540) at several JNJ-64619178 concentrations. Hatched bars depict symmetric arginine dimethylation of SmD1/3 (SmD1/3-Me2, 10 nmol/L JNJ-64619178) monitored by immunoblotting. Quantification was normalized to β-actin. Error bars represent mean ± standard deviation (SD).