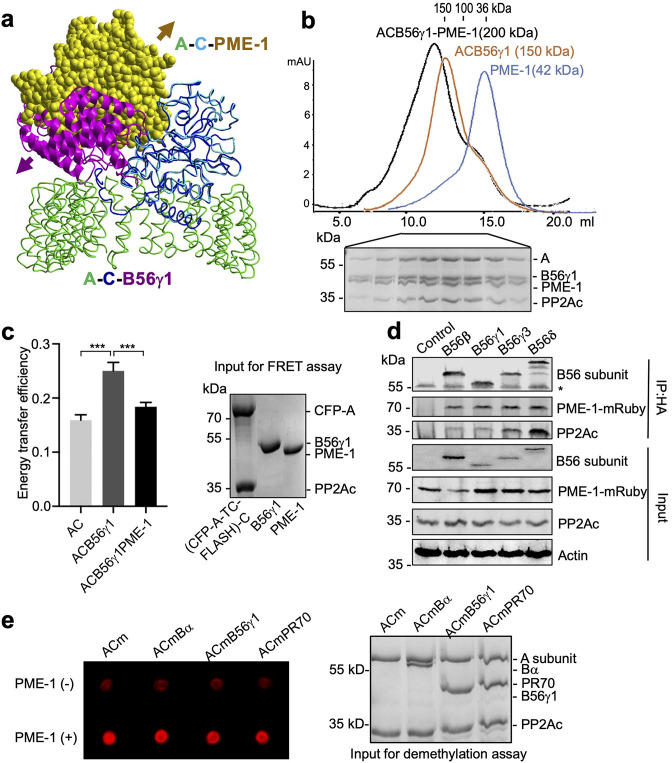
Figure 1. PP2A methylesterase 1 (PME-1) directly interacts with and demethylates protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) holoenzymes.
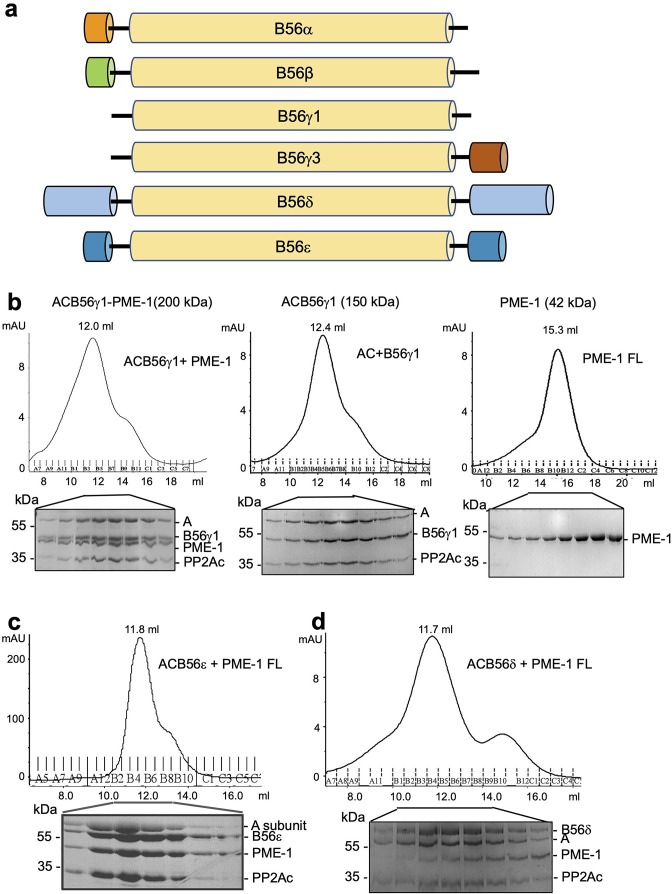
(a) Structural overlay of the PP2A-B56γ1 holoenzyme (PDB code: 2NPP) to the PP2A core enzyme–PME-1 complex (PDB code: 3C5W) aligned via PP2Ac (c) and the C-terminal five huntingtin-elongation-A-subunit-TOR (HEAT) repeats of the A-subunit. Arrows indicate the directions of movements of PME-1 and B56γ1 needed to avoid clashes in the overlaid structures. (b) The overlaid gel filtration profiles of the PP2A-B56γ1 holoenzyme with PME-1 (black), PP2A core enzyme (AC) with B56γ1(orange), and PME-1 alone (blue). The sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) data examining protein fractions for the PP2A-B56γ1 holoenzyme with PME-1 were provided below. The molecular weight standards for gel filtration chromatography were generated using the PP2A free catalytic subunit (36 kDa), the PP2A core enzyme (100 kDa), and the PP2A-B56γ1 holoenzyme (150 kDa). (c) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay measured changes in the distance between the A-subunit N- and C-termini in the PP2A core enzyme before and after the addition of B56γ1 with and without PME-1 (left). Representative results were shown with mean ± standard deviation (SD) calculated from three experimental repeats. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparisons was used to determine the difference between independent groups (***p < 0.001). Protein inputs used in FRET assay were examined by SDS–PAGE and visualized by Coomassie blue staining (right). (d) Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of PME-1-mRuby and PP2Ac by HA-tagged B56 (B56β, B56γ1, B56γ3, and B56δ) recombinantly expressed in HEK 293T cells. The band with * is the heavy chain of anti-HA antibody. (e) PME-1 catalyzes demethylation of methylated core enzyme and holoenzymes in vitro. The level of demethylation was determined by 4b7 antibody that specifically recognizes the unmethylated PP2Ac (left). Inputs of PP2A complexes were examined as in c (right).