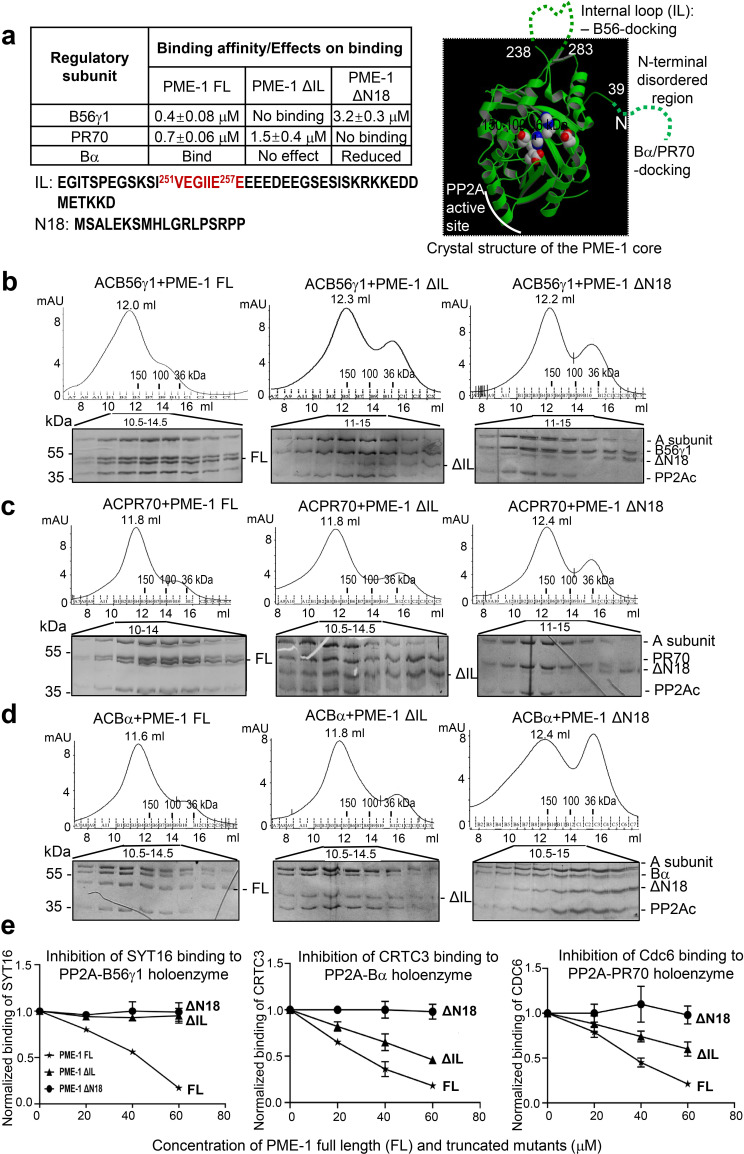
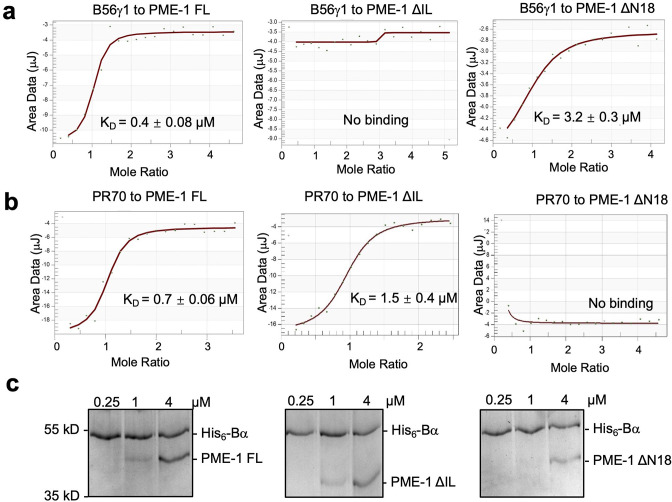
Figure 2. Mapping of PP2A methylesterase 1 (PME-1) interactions with protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulatory subunits and holoenzymes.
(a) Summary of mapping results (Figure 2—figure supplement 1) on the roles of PME-1 disordered regions in interactions with different PP2A regulatory subunits (left) and illustration of disordered regions (dashed lines) and their contributions on the crystal structure of the apo-PME-1 structured core (PDB code: 3C5V) (right). Sequences of PME-1 internal loop (IL) and N-terminal 18 residues (N18) were shown, highlighting a substrate-mimicking B56 short linear motif (SLiM) in IL (lower left). The boundary residue numbers for the disordered regions are labeled, and the PME-1 active site residues are highlighted in spheres (right). Comigration of PP2A-B56γ1 (b), PP2A-PR70 (c), or PP2A-Bα (d) holoenzymes with PME-1 FL, ΔIL, or ΔN18 over gel filtration chromatography. Protein fractions with the indicated ranges of elution volumes were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. The molecular weight standards for gel filtration chromatography are generated as in Figure 1b. (e) PME-1 concentration-dependent inhibition of substrate peptide binding to specific holoenzymes. Inhibition curves against GST-SYT16 (132KLPHVLSSIAEEEHH147L) binding to PP2A-B56γ1 (left), GST-CRTC3 (380SGPSRRRQPPVSPLTLSPGPE401A) binding to PP2A-Bα (middle), and GST-Cdc6 (49KALPLSPRKRLG DDNLCNTPHLPPCSPPKQGK KENGPPHSH90T) to PP2A-PR70 (right) by PME-1 FL, ΔN18, or ΔIL were generated from competitive pulldown data in Figure 2—figure supplement 3a. Values for all data points on the inhibition curves are mean ± standard deviation (SD) from three experimental repeats.