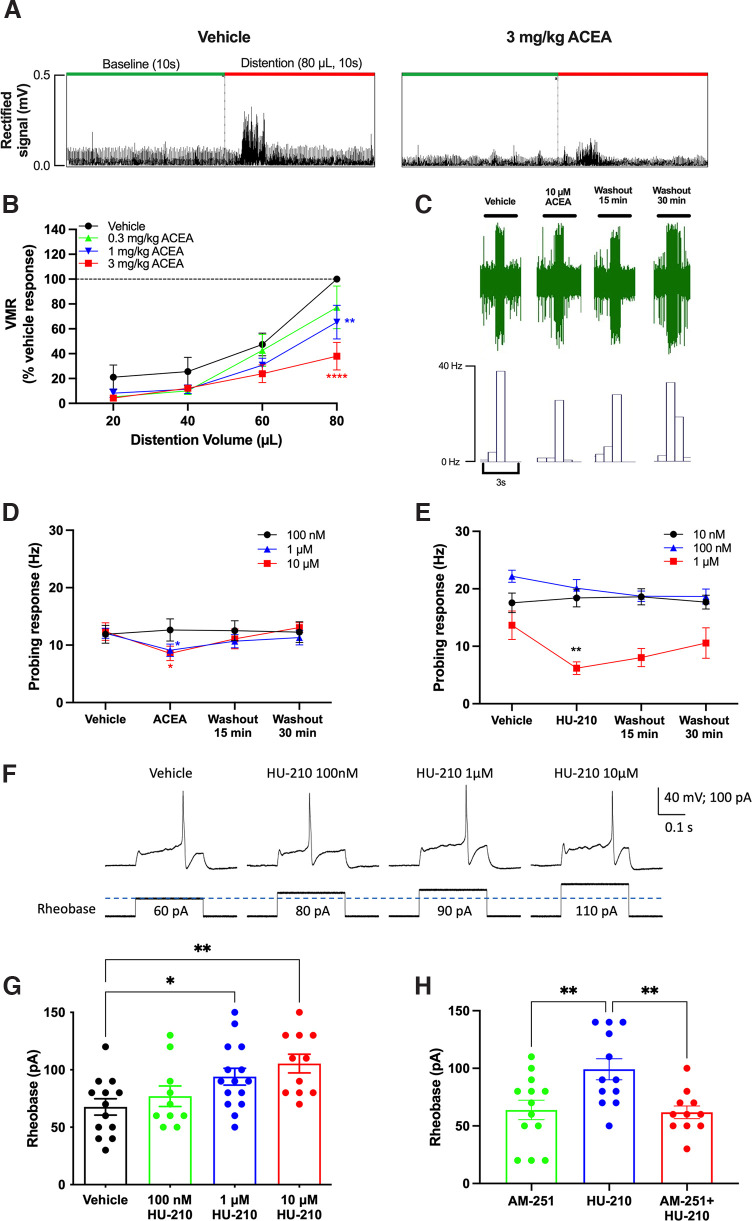
Figure 1.
CB1R agonists ACEA and HU-210 dose-dependently reduced VMR, colonic afferent nerve mechanosensitivity, and DRG neuronal excitability. A, A representative recording showing the effect of ACEA (3 mg/kg) on EMG activity to CRD (10 s, 80 µl). B, ACEA dose-dependently reduced VMR to CRD (N = 7). C, A representative recording showing the effect of ACEA (10 μm) on colonic afferent nerve responses to probing with a 1 × g von Frey filament. D, ACEA (1 and 10 μm) significantly reduced colonic mechanosensitivity to probing (1 μm: p = 0.0494, 10 μm: p = 0.0202), while a lower concentration (100 nm) had no effect (n = 8-10). E, HU-210 (1 μm) significantly reduced colonic mechanosensitivity to probing with von Frey filament (p = 0.0046), while lower concentrations (10 and 100 nm) had no effect (p > 0.9999 for both). F, Representative recordings showing the effect of HU210 on DRG neuron excitability. HU-210 (1 and 10 μm) increased the rheobase (i.e., decrease excitability) of DRG neurons (1 μm: p = 0.044, 10 μm: p = 0.0047) (G), and this effect was blocked by AM-251 (p = 0.0058) (H). *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ****p < 0.0001.