Figure 3: Probenecid treatment alters the urine metabolome.
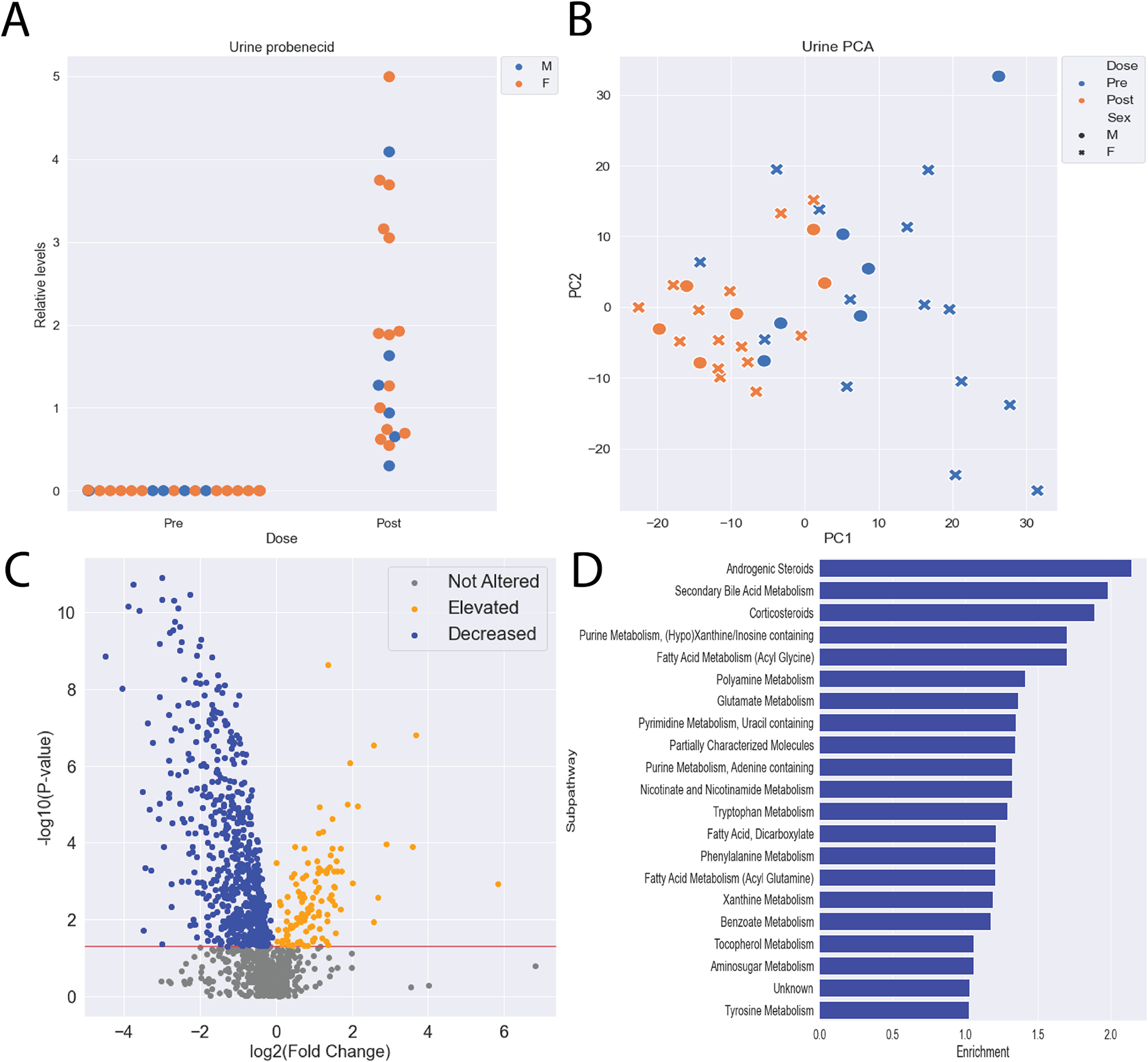
A) Probenecid levels in the urine were significantly elevated 5 hours after oral dosage in all participants. B) Principal component analysis reveals separation between pre and post treatment with probenecid urine metabolomes. C) Hundreds of metabolites were significantly altered following treatment with probenecid, with most being decreased. D) Among the significantly decreased metabolites, 23 subpathways with at least 5 metabolites were enriched, including subpathways traditionally associated with OAT-mediated transport (Secondary Bile Acid Metabolism, Tryptophan Metabolism, Phenylalanine Metabolism, etc.).
