Figure 5: Presumed inhibition of urate reuptake transporters such as URAT1 led to a specific drug-metabolite interaction between probenecid and urate.
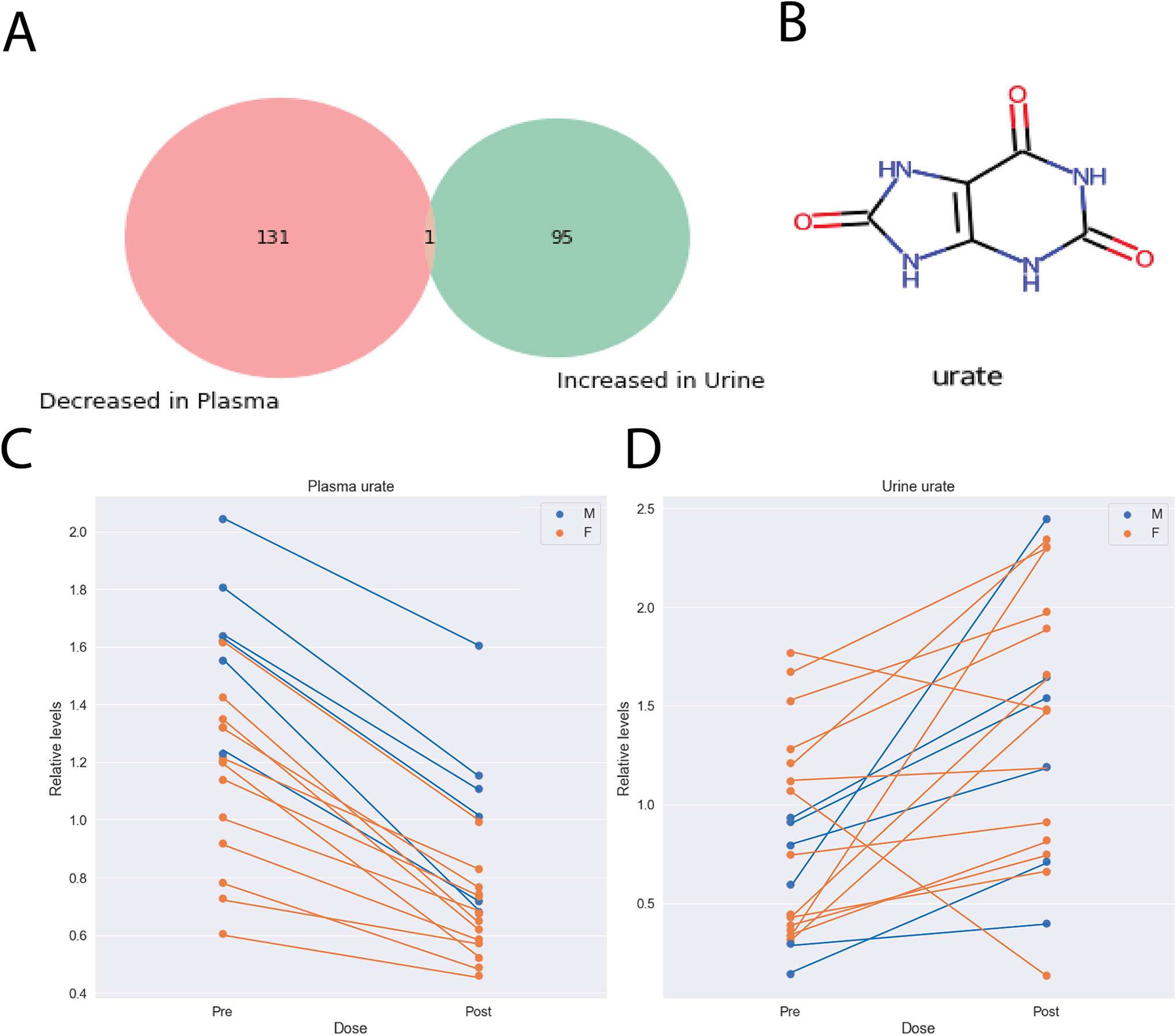
A) Urate was the only metabolite to be significantly decreased in the plasma (fold change < 0.8) and increased in the urine (fold change > 1.25) with more selective fold change criteria. B) The chemical structure for urate. C) Urate levels were significantly decreased in the plasma following treatment with probenecid (p-value: 1.20E-10, fold change: 0.606). D) Urate levels were significantly increased in the urine following treatment with probenecid (p-value: 0.008, fold change: 1.705).
