Figure 1. Illustration of 17-epi-NPD1/17-epi-PD1 proposed biosynthesis, actions, and synthetic strategy.
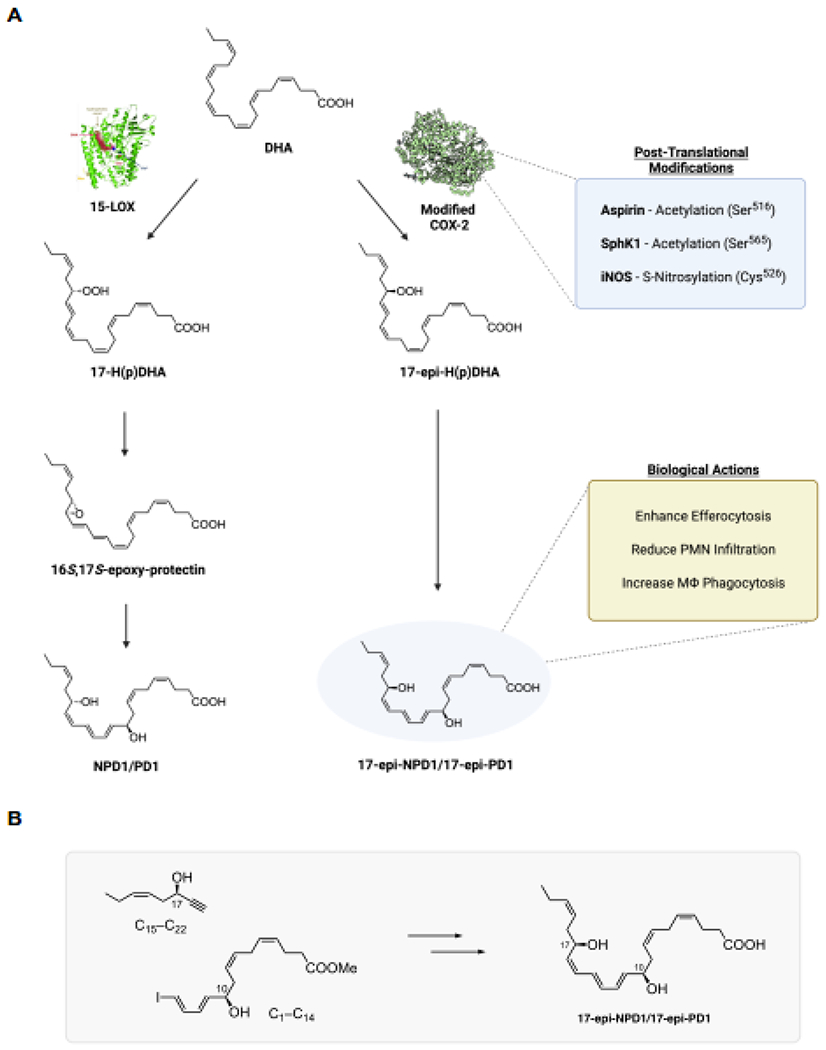
(A) Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is converted to 17S-H(p)DHA via 15-lipoxygenase to produce NPD1/PD1 [5, 8] via cell-type dependent pathways. For illustration, in silico Pseudomonas aeruginosa-derived 15-lipoxygenase crystal structure is shown docked with DHA from [47]. Also, DHA can be converted to 17R-H(p)DHA via the acetylation of COX-2 by aspirin (PDB 5F19, crystal structure from [48]. The 17R-hydroperoxide undergoes enzymatic epoxidation followed by enzymatic hydrolysis to 17-epi-NPD1/17-epi-PD1; see [26]. COX-2 undergoes post-translational modifications that include acetylation and nitrosylation demonstrated in [27, 49, 50]. Figure illustration was created with Biorender.com. (B) A convergent synthetic approach of 17-epi-NPD1/17-epi-PD1 from two main precursors (see results section 3). Structures were made using ChemDraw level professional version 20.1.0.112 (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
