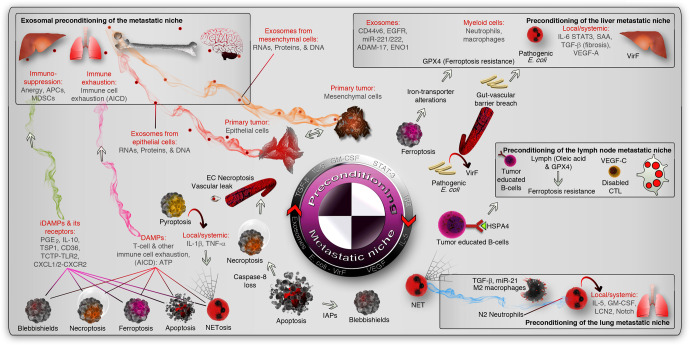
Fig. 4.
Preconditioning of the metastatic niche. The epithelial and mesenchymal cells precondition the metastatic niche (marked by inset boxes) by cytokine or chemokine secretion or primarily through exosomes (red and orange smoky trails, respectively. The liver, lymph node, and lung metastatic niche were shown as examples (inset boxes). Microbial preconditioning of the liver niche is shown as an example (pathogenic vir-F containing E. coli), and exosomal and immunological preconditioning is also shown in the liver niche. In the lymph node niche, tumor-educated immune cells (B-cells exposed to HSPA4 from tumors) or VEGF-C induced exhaust of cytotoxic T- cells (CTLs) or lymph-protected tumor cells serve as preconditioning mediators (non-exhaustive list of mechanisms). In the lungs, polarized immune cells (into pro-tumor) precondition the niche by cytokines and lipocalin-2 (LCN2). In the cell death context, DAMPs or iDAMPs induce cytotoxic immune cell exhaustion by AICD or immunosuppression, respectively (magenta and green smoke trails, respectively). AICD activation-induced cell death, EC necroptosis endothelial cell necroptosis, MDSCs myeloid-derived suppressor cells, APCs antigen-presenting cells, PGE2 prostaglandin-E2, TSP1 thrombospondin-1, TLR2 Toll-like receptor-2, IAPs inhibitor of apoptotic proteins, NET neutrophil extracellular trap