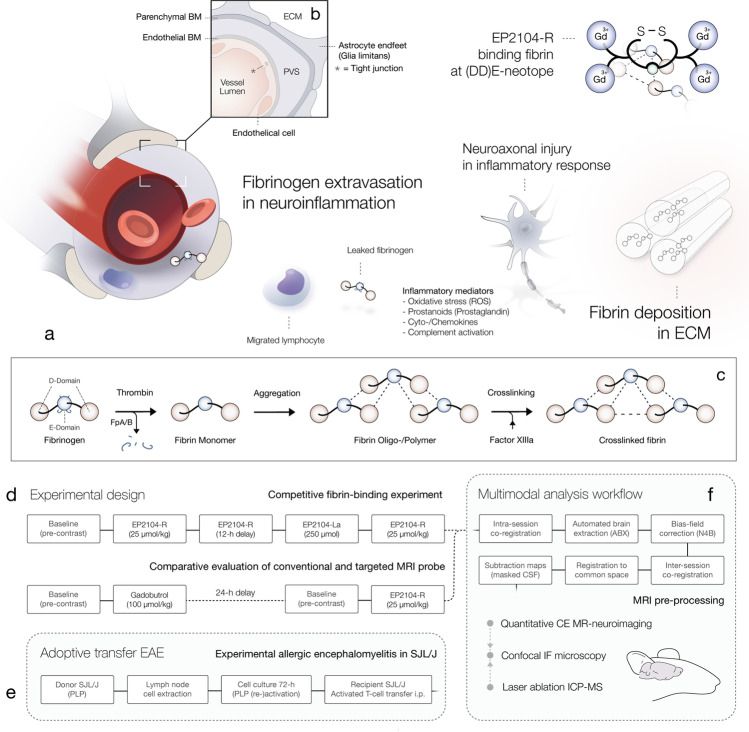
Fig. 1.
Fibrin deposition in inflammatory CNS disorders. Dysfunction of the BBB is a hallmark of acute CNS inflammation and one of the earliest events in the pathophysiology of several CNS disorders. Increased barrier permeability is accompanied by extravasation of plasma components and small externally administered compounds into the interstitial space (see a) and results in fibrin(ogen) deposition in the perivascular space (PVS) and ECM, which promotes inflammatory response and immune migration into the CNS. Panel b demonstrates a cross section of the neurovascular unit, which depicts the ensemble of tight junctions, endothelial cells, basement membranes (BM) and astrocytic endfeet that implements the barrier function. Panel c shows the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin within the coagulation pathway. In the inflammatory component of various CNS diseases, such as MS, aberrant or auto-reactive leucocytes migrate into the CNS. Migrated immune cells promote further CNS migration of peripheral monocytes/macrophages, which accumulate in the PVS and eventually migrate into the interstitial space. Activated peripheral and resident immune cells form clusters around CNS entry points and induce neuroaxonal injury. EP2104-R, a peptide-conjugated Gd-based (Gd3+) positive contrast agent, binds fibrin with high affinity, which is visualised and quantified using molecular MRI. Panel d demonstrates experimental designs for the competitive fibrin binding assay and comparative evaluation of EP2104-R and a clinically used (non-targeted) MRI contrast agent. Panel e illustrates the induction of murine adoptive-transfer EAE model, a common model for MS. Epitope-primed and (re-)activated T-cells from SJL/J donor mice, immunised with PLP, were transferred to naïve syngeneic recipients, which rapidly develop a characteristic inflammatory demyelinating CNS disorder. Last panel (f) illustrates the multimodal analysis workflow for validation of imaging findings from quantitative (contrast-enhanced) MRI with immunofluorescence confocal microscopy (IF-CM) and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP MS). BM, basement membrane; ECM, extracellular matrix; PVS, perivascular space; ROS, reactive oxygen species; FpA/B, fibrinopeptide A/B; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; PLP, proteolipid