Figure 4.
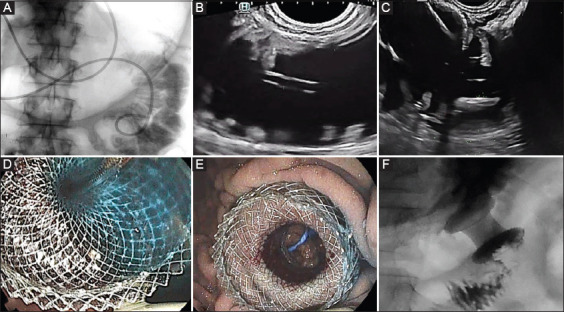
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided gastroenterostomy with the wireless endoscopic simplified technique. (A) Endoscopic placement of an orojejunal tube bypassing the stenosis for controlled injection of saline, with or without contrast dye (e.g., indigo carmine). (B) EUS-guided identification of a dilated jejunal loop containing the orojejunal tube. (C) Freehand release of the distal flange of an electrocautery-enhanced lumen-apposing metal stent (LAMS) inside the jejunum. (D) Release of the proximal flange of the LAMS with blue-dyed liquid aspirated into the stomach through the LAMS. (E) LAMS after pneumatic dilation, with jejunal mucosa and the orojejunal tube visible through the stent. (F) contrast injection through the orojejunal tube can be aspirated into the stomach through the LAMS without leakage
