Figure 1.
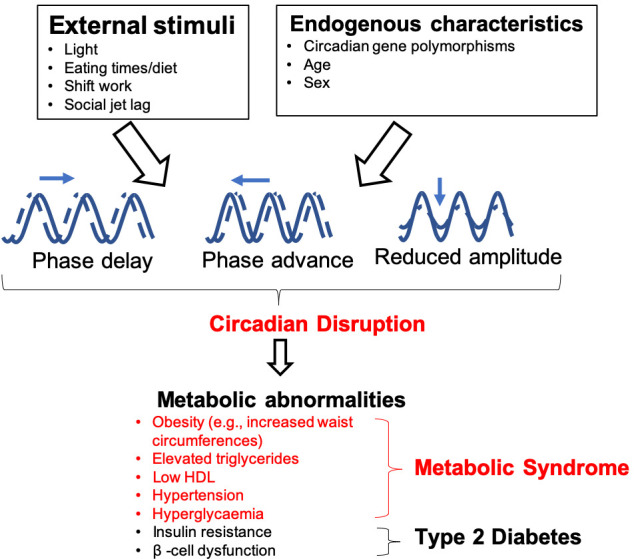
Influences on, and consequences of, circadian rhythm disruption. Both endogenous and external factors can predispose individuals to circadian disruption. This can cause dysfunction of peripheral oscillators, which are involved in the regulation of metabolic functions such as body weight homeostasis, glucose metabolism and β-cell function. Individuals who experience circadian disruption, which may be through phase delays/advances or by changes in amplitude (difference between peak and trough of the rhythms) are at an elevated risk of developing metabolic abnormalities, which can lead to metabolic syndrome and T2DM.
